Lead(II) oxide
Lead(II) oxide, also known as lead monoxide or litharge, is a chemical compound with the formula PbO. It is a yellowish or reddish crystalline solid that is commonly used in various industrial applications. In this article, we will explore the properties, uses, and safety considerations of Lead(II) oxide.
Properties
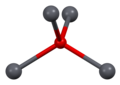
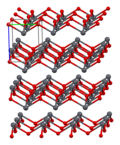
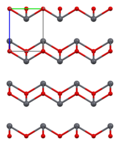
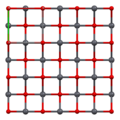
Lead(II) oxide has a molecular weight of 223.2 g/mol and a melting point of 888°C. It is insoluble in water but soluble in acids, forming lead salts. The compound exists in two polymorphs: litharge, which has a tetragonal crystal structure, and massicot, which has an orthorhombic structure.
Uses
Lead(II) oxide has a wide range of applications across different industries. One of its primary uses is in the production of lead-acid batteries, where it serves as a component of the positive electrode (anode). The compound helps to convert lead sulfate into lead dioxide during the charging process, allowing the battery to store and release electrical energy efficiently.
Another significant application of Lead(II) oxide is in the manufacturing of glass and ceramics. It acts as a flux, reducing the melting point of the materials and improving their workability. Additionally, the compound is used as a pigment in the production of yellow and red paints, as well as in the coloring of glassware.
Lead(II) oxide also finds use in the field of electronics. It is employed in the production of semiconductors, particularly in the fabrication of certain types of diodes and transistors. The compound's electrical properties make it suitable for these applications.
Safety Considerations
It is important to note that Lead(II) oxide is toxic and poses health risks if not handled properly. Inhalation or ingestion of the compound can lead to lead poisoning, which can cause severe health issues, especially in children and pregnant women. Therefore, it is crucial to follow safety guidelines and use appropriate protective equipment when working with or around Lead(II) oxide.
See Also
References
Lead(II) oxide
- PbOlabel.jpg
Lead(II) oxide
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD