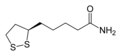
Lipoamide
Lipoamide is a coenzyme that plays a crucial role in various metabolic processes within the human body. It is an essential component of several enzyme complexes, including pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, which are involved in energy production through the citric acid cycle.
Structure and Function
Lipoamide, also known as lipoic acid or thioctic acid, is a sulfur-containing compound with a unique structure. It consists of a five-membered ring with two sulfur atoms at adjacent positions. This structure allows lipoamide to act as a versatile cofactor in enzymatic reactions.
Lipoamide functions as a carrier of acyl groups during metabolic reactions. It undergoes reversible oxidation and reduction reactions, shuttling acetyl groups between different enzymes. This process is crucial for the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA, which is a key step in the metabolism of carbohydrates.
Role in Energy Production
One of the primary functions of lipoamide is its involvement in energy production. It acts as a cofactor for the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which converts pyruvate, a product of glycolysis, into acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA then enters the citric acid cycle, where it is further oxidized to generate ATP, the main energy currency of the cell.
Lipoamide also plays a vital role in the alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, which is involved in the metabolism of amino acids. This complex converts alpha-ketoglutarate, a product of amino acid breakdown, into succinyl-CoA, another intermediate in the citric acid cycle.
Clinical Significance
Lipoamide deficiency can lead to various metabolic disorders. For example, defects in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which relies on lipoamide as a cofactor, can result in a condition called pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency. This disorder impairs the body's ability to convert pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, leading to a buildup of pyruvate and lactic acid in the blood, causing neurological symptoms.
Lipoamide has also gained attention for its potential therapeutic benefits. It exhibits antioxidant properties and has been studied for its role in reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. Additionally, lipoamide supplementation has shown promise in the management of certain conditions, such as diabetic neuropathy.
References
<references>
See Also
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD