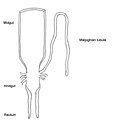
Malpighian tubule system
Malpighian Tubule System
The Malpighian tubule system is an essential excretory and osmoregulatory system found in some invertebrates, including most arthropods such as insects and some arachnids. This system is notably absent in aquatic arthropods. It plays a crucial role in the removal of nitrogenous wastes and the regulation of water and electrolyte balance.
Structure and Function
The Malpighian tubule system consists of blind-ended tubes that extend from the alimentary canal, specifically the junction between the midgut and hindgut. The number of tubules varies among different species, ranging from only a few to several hundred. These tubules are bathed in hemolymph, the arthropod equivalent of blood, which allows for the direct exchange of substances.
The primary function of the Malpighian tubules is to filter metabolic wastes, such as uric acid, from the hemolymph. These wastes are then converted into a less toxic form, usually solid or semi-solid, which is excreted into the gut and eliminated with feces. This process helps in conserving water, a critical adaptation for terrestrial life.
In addition to waste excretion, the Malpighian tubule system also plays a role in osmoregulation. By actively transporting ions and other solutes from the hemolymph into the tubules, it controls the osmotic pressure and ionic composition of body fluids.
Comparative Anatomy and Evolution
The Malpighian tubule system is considered an evolutionary adaptation to terrestrial living. Its ability to conserve water while eliminating wastes efficiently is crucial for survival in dry environments. Comparative studies of the Malpighian tubule system across different arthropod groups provide insights into the evolutionary pressures and adaptations associated with terrestrial life.
Pathology
While the Malpighian tubule system is robust, it can be affected by various pathogens and environmental toxins. Insects, for example, may suffer from infections or blockages in the tubules, leading to osmoregulatory imbalances and accumulation of toxic wastes.
Research and Applications
Research on the Malpighian tubule system has applications in pest control, where understanding the system's function can lead to the development of targeted insecticides that disrupt waste elimination or osmoregulation in pest species.
See Also
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD