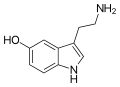
Neuromodulation
Neuromodulation is a technology that acts directly upon nerves. It is the alteration—or modulation—of nerve activity by delivering electrical or pharmaceutical agents directly to a target area. Neuromodulation devices and treatments are life changing. They affect every area of the body and treat nearly every disease or symptom from headaches to tremors to spinal cord damage to urinary incontinence.
Types of Neuromodulation
Neuromodulation can be used to treat a wide range of conditions, including chronic pain, movement disorders, spasticity, and epilepsy. There are several types of neuromodulation, including:
- Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS): This is the most common type of neuromodulation, used to treat chronic pain conditions such as failed back surgery syndrome, complex regional pain syndrome, and peripheral neuropathy.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): This is used to treat movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease, essential tremor, and dystonia.
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS): This is used to treat epilepsy and depression.
- Sacral Nerve Stimulation (SNS): This is used to treat urinary and fecal incontinence.
Benefits of Neuromodulation
Neuromodulation has several benefits, including:
- It can provide significant relief from chronic pain.
- It can improve quality of life for people with movement disorders.
- It can reduce the frequency and severity of seizures in people with epilepsy.
- It can help control urinary and fecal incontinence.
Risks and Side Effects
Like any medical procedure, neuromodulation carries some risks and potential side effects. These can include infection, bleeding, headache, and discomfort at the site of the implanted device. However, most side effects can be managed with medication or adjustments to the device.
Future of Neuromodulation
The field of neuromodulation is rapidly evolving, with new technologies and treatments being developed all the time. Future advancements may include more precise targeting of nerve signals, wireless devices, and treatments for conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, and tinnitus.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD