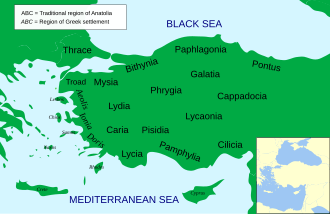
Phrygia
Phrygia was an ancient kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Turkey, centered around the Sakarya River. The Phrygians were an Indo-European people who settled in the region around 1200 BCE, following the collapse of the Hittite Empire. The kingdom of Phrygia reached its peak during the 8th century BCE under the rule of King Midas, who is famously associated with the myth of the "Midas touch."
History
Phrygia's early history is closely linked with the Bronze Age collapse, which saw the decline of several major civilizations in the eastern Mediterranean. The Phrygians established their capital at Gordion, which became a significant cultural and political center. The kingdom was known for its advanced metalworking and textile production.
During the 8th century BCE, Phrygia became a dominant power in Anatolia. King Midas, the most famous Phrygian ruler, is often associated with wealth and prosperity. However, the kingdom faced numerous challenges, including invasions by the Cimmerians in the late 7th century BCE, which led to its decline.
Culture
Phrygian culture was heavily influenced by neighboring civilizations, including the Hittites, Greeks, and Lydians. The Phrygians are credited with significant contributions to art, music, and religion. They worshipped a pantheon of gods, with the mother goddess Cybele being one of the most important deities.
Phrygian art is characterized by intricate metalwork, pottery, and textiles. The Phrygians also had a unique style of music, which was later adopted by the Greeks. The Phrygian cap, a soft, conical hat, became a symbol of freedom and was later adopted by various revolutionary movements.
Archaeology
The most significant archaeological site in Phrygia is Gordion, where extensive excavations have revealed a wealth of information about Phrygian society. The site includes the remains of the royal citadel, monumental tombs, and various artifacts that provide insight into the daily life and culture of the Phrygians.
Legacy
Phrygia's influence persisted long after its decline. The region was eventually absorbed into the Lydian Empire, and later the Achaemenid Empire. The legacy of Phrygia can be seen in various aspects of ancient and modern culture, including mythology, art, and music.
Related Pages
This article is a Ancient Near East–related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD