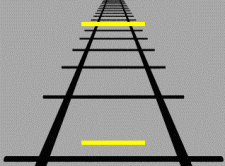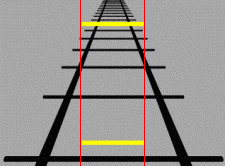
Ponzo illusion
Ponzo Illusion is a visual illusion that was first demonstrated by the Italian psychologist Mario Ponzo in 1911. He suggested that the human mind judges an object's size based on its background. He showed this by drawing two identical lines across a pair of converging lines, similar to railway tracks. The upper line looks longer than the lower line, although they are both the same length. This illusion is an example of a perspective illusion.
Overview
The Ponzo Illusion capitalizes on the brain's system of judging depth and distance. In the classic illustration of this illusion, two horizontal lines of identical length are placed over a background of converging lines, such as a drawing of a road or railway tracks receding into the distance. The upper horizontal line appears longer than the lower one because our brain interprets the background cues as indicating that the upper line is farther away. Since both lines are actually the same size, our brain concludes that the line that appears farther away must be longer in order to maintain its size at that distance.
Mechanism
The underlying mechanism of the Ponzo Illusion involves the human perception system, which is influenced by linear perspective. Linear perspective is a depth cue that allows our brain to interpret the size of objects in the context of their perceived distance. When the converging lines suggest depth, objects placed in that context are perceived relative to that depth. This is why the Ponzo Illusion is often categorized under monocular cues, which are depth cues that can be perceived by one eye alone.
Applications and Significance
The Ponzo Illusion is more than just a curious visual trick; it has applications and significance in various fields such as psychology, neuroscience, and even design and art. In psychology and neuroscience, it helps researchers understand how the human brain processes visual information and how depth perception and size constancy work. In design and art, understanding this illusion can help artists and designers create more effective and engaging visual compositions by manipulating perspective to influence perception.
Related Illusions
The Ponzo Illusion is related to other visual illusions that involve perspective and depth cues, such as the Müller-Lyer Illusion, the Hering Illusion, and the Zöllner Illusion. Each of these illusions demonstrates different ways in which our perception of size, length, or direction can be distorted by contextual visual cues.
Conclusion
The Ponzo Illusion remains a fascinating topic in the study of visual perception, illustrating how our brains interpret visual information based on context and background cues. It underscores the complexity of the perceptual processes and the ways in which our environment can shape our perception of reality.
This article is a psychology-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD