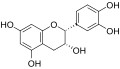
Procyanidin
A class of flavonoids with antioxidant properties
Procyanidins are a class of flavonoids that are widely distributed in the plant kingdom. They are known for their antioxidant properties and are found in a variety of foods and beverages, including grapes, apples, chocolate, and red wine.
Structure and Classification
Procyanidins are a type of polyphenol and belong to the larger class of flavan-3-ols. They are oligomeric compounds, meaning they are composed of multiple monomer units. The basic monomer unit of procyanidins is catechin or epicatechin, which are linked together by carbon-carbon bonds.
Procyanidins are classified based on the number of monomer units:
- Monomers: Single catechin or epicatechin units.
- Dimers: Two monomer units linked together.
- Oligomers: Three to ten monomer units.
- Polymers: More than ten monomer units.
Sources of Procyanidins
Procyanidins are found in a variety of plant-based foods and beverages. Some of the richest sources include:
- Grapes: Both the seeds and skins of grapes contain high levels of procyanidins, which are also present in red wine.
- Apples: Particularly the skins, are a good source of procyanidins.
- Chocolate: Especially dark chocolate, contains significant amounts of procyanidins.
- Berries: Such as blueberries, cranberries, and strawberries.
Health Benefits
Procyanidins are known for their potential health benefits, primarily due to their antioxidant properties. Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals, which can cause oxidative stress and damage to cells.
Cardiovascular Health
Procyanidins have been studied for their role in promoting cardiovascular health. They may help improve endothelial function, reduce blood pressure, and decrease LDL cholesterol oxidation, which is a risk factor for atherosclerosis.
Anti-inflammatory Effects
These compounds also exhibit anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial in reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as arthritis and diabetes.
Cancer Prevention
Some studies suggest that procyanidins may have a role in cancer prevention by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and inducing apoptosis.
Mechanism of Action
The beneficial effects of procyanidins are largely attributed to their ability to scavenge free radicals and chelate metal ions, thereby preventing oxidative damage. They also modulate various signaling pathways involved in inflammation and cell proliferation.
Consumption and Bioavailability
The bioavailability of procyanidins can vary depending on the food source and the form in which they are consumed. Factors such as food processing and preparation can affect their absorption and metabolism in the body.
Related Pages
Procyanidin
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD