Stem rust
(Redirected from Puccinia graminis)
Stem Rust
Stem rust, also known as black rust, is a significant fungal disease that affects cereal crops, particularly wheat, barley, and rye. It is caused by the fungus Puccinia graminis, which has a complex life cycle involving two hosts and several spore stages. Stem rust is notorious for its ability to cause severe yield losses in susceptible crops, making it a major concern for agriculture worldwide.
Life Cycle
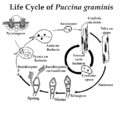
The life cycle of Puccinia graminis is heteroecious, meaning it requires two different host plants to complete its life cycle. The primary host is cereal crops, while the alternate host is typically a species of the genus Berberis (barberry).
Spore Stages
1. Urediniospores: These are the repeating spores that spread the infection during the growing season. They are produced on the cereal host and can reinfect the same host, leading to multiple cycles of infection.
2. Teliospores: These are thick-walled spores that form at the end of the growing season. They overwinter on the cereal host and germinate in the spring to produce basidiospores.
3. Basidiospores: These spores infect the alternate host, Berberis. They are produced from the germination of teliospores.
4. Aeciospores: These are produced on the alternate host and can infect the cereal host, completing the cycle.
Symptoms
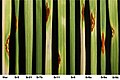
Stem rust is characterized by the appearance of reddish-brown pustules on the stems, leaves, and sometimes the heads of infected plants. These pustules contain urediniospores, which are responsible for spreading the disease. As the disease progresses, the pustules turn black as teliospores develop.
Economic Impact
Stem rust can cause significant yield losses, particularly in susceptible wheat varieties. In severe cases, it can lead to total crop failure. The disease has historically caused major epidemics, such as the one in the United States in the 1950s, which led to the development of resistant wheat varieties.
Management Strategies
1. Resistant Varieties: The development and use of resistant wheat varieties is one of the most effective strategies for managing stem rust.
2. Cultural Practices: Removing the alternate host, Berberis, can help break the life cycle of the fungus and reduce the incidence of the disease.
3. Fungicides: The application of fungicides can help control stem rust, especially in areas where resistant varieties are not available.
Recent Developments
In recent years, new races of stem rust, such as Ug99, have emerged, which can overcome the resistance of many previously resistant wheat varieties. This has renewed interest in breeding for resistance and developing integrated management strategies.
Also see
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD