Punic Wars
Punic Wars
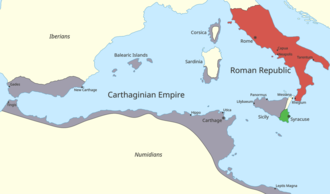
The Punic Wars were a series of three major conflicts fought between the Roman Republic and the Carthaginian Empire, two of the most powerful states of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC. These wars were among the largest wars of the ancient world and are crucial to understanding the development of Roman military and naval power, as well as the establishment of Rome as a dominant empire in the Mediterranean region.
First Punic War (264–241 BC)
The First Punic War began in 264 BC and was primarily a naval conflict. The war erupted over the control of Sicily, a strategically crucial island in the Mediterranean Sea. Despite being a land power, Rome built a large fleet to challenge Carthage's well-established naval dominance. The war saw several significant battles, including the Battle of Agrigentum and the naval Battle of the Aegates Islands. The war ended in 241 BC with the defeat of Carthage and the signing of the Treaty of Lutatius, which forced Carthage to cede Sicily to Rome and pay a large indemnity.
Second Punic War (218–201 BC)
The Second Punic War, often remembered for the Carthaginian general Hannibal's crossing of the Alps, began in 218 BC. Hannibal's invasion of Italy was a bold and innovative strategy that brought the war to the Roman heartland. Despite winning several battles, including the famous Battle of Cannae, Hannibal could not secure a decisive victory. Rome, under the leadership of generals like Scipio Africanus, took the fight to North Africa, leading to the decisive Battle of Zama in 202 BC. This battle ended Carthage's role as a major power and imposed harsh terms, including loss of territories and a crippling war indemnity.
Third Punic War (149–146 BC)
The Third Punic War was initiated by Rome under the pretext of a breach of the treaty by Carthage. By this time, Carthage had recovered economically but was militarily weak. In 149 BC, Rome laid siege to Carthage, and after three years of fighting, the city was destroyed in 146 BC. The surviving inhabitants were sold into slavery, and the territory became the Roman province of Africa. This war marked the end of Carthaginian power and the beginning of Roman hegemony over the western Mediterranean.
Impact of the Punic Wars
The Punic Wars had a profound impact on Rome and the Mediterranean world. They marked the rise of Rome as the dominant military power, leading to its expansion into Greece, the eastern Mediterranean, and parts of North Africa. The wars also led to significant military innovations, including the development of the Roman navy and tactics. Economically and socially, the wars contributed to changes in Roman society, including the increase of slavery and the concentration of wealth in the hands of a few.
See Also
The Punic Wars, through their scale and outcome, significantly shaped the course of Western history, laying the groundwork for the Roman Empire's expansion and its cultural and political legacy in Europe and beyond.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD