Rhizopus microsporus
Rhizopus microsporus is a species of fungus in the genus Rhizopus. It is known for its role in food spoilage, plant pathology, and as an opportunistic pathogen in humans. This species is also notable for its use in the production of certain fermented foods.
Taxonomy and Classification
Rhizopus microsporus belongs to the kingdom Fungi, phylum Zygomycota, class Zygomycetes, order Mucorales, and family Mucoraceae. It is closely related to other species within the genus Rhizopus, such as Rhizopus stolonifer.
Morphology
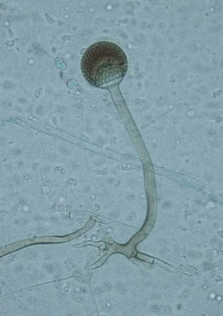
Rhizopus microsporus is characterized by its hyphae, which are typically non-septate and can grow rapidly. The sporangia are spherical and contain numerous sporangiospores. The sporangiophores are unbranched and arise from the rhizoids.
Ecology and Habitat
This fungus is commonly found in soil, decaying organic matter, and various food products. It thrives in warm and humid environments, making it a frequent contaminant in tropical and subtropical regions.
Pathogenicity
Rhizopus microsporus is an opportunistic pathogen that can cause zygomycosis in humans, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. It can also infect plants, leading to diseases such as soft rot in fruits and vegetables.
Industrial and Food Applications
In some cultures, Rhizopus microsporus is used in the production of traditional fermented foods. For example, it is involved in the fermentation process of tempeh, a popular Indonesian food made from soybeans.
Life Cycle
The life cycle of Rhizopus microsporus includes both asexual and sexual reproduction. Asexually, it reproduces through the formation of sporangia that release sporangiospores. Sexually, it forms zygospores through the fusion of specialized hyphae from compatible mating types.
Control and Prevention
Controlling the spread of Rhizopus microsporus involves maintaining proper hygiene and storage conditions, especially in food production and healthcare settings. Antifungal treatments may be necessary for infections in humans.
See Also
References
External Links
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD