Sandwich compound
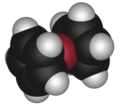
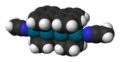
Sandwich compounds are a class of organometallic compounds characterized by a metal atom sandwiched between two aromatic rings. The most famous example of a sandwich compound is ferrocene, where an iron (Fe) atom is sandwiched between two cyclopentadienyl (Cp) rings. These compounds belong to a broader class of compounds known as metallocenes. Sandwich compounds play a crucial role in the field of organometallic chemistry, with applications ranging from catalysis to the development of new materials.
Structure and Bonding
The structure of sandwich compounds involves a central metal atom or ion that is coordinated in a parallel fashion by two cyclic ligands. These ligands are typically aromatic, contributing to the stability of the compound through π-bonding. The bonding in sandwich compounds can be described by the 18-electron rule, which is often used to predict the stability of organometallic compounds. In this context, the metal atom contributes its valence electrons, while each ligand typically contributes six electrons from its π system to the bonding.
Classification
Sandwich compounds can be classified based on the type of metal and the ligands involved. The most common types include:
- Ferrocenes: With iron as the central metal and cyclopentadienyl rings as ligands.
- Ruthenocenes: Similar to ferrocenes but with ruthenium instead of iron.
- Cobaltocenes: Featuring cobalt as the central metal.
- Nickelocenes: With nickel as the central metal.
Additionally, variations exist where the ligands are not identical, leading to unsymmetrical sandwich compounds.
Synthesis
The synthesis of sandwich compounds typically involves the reaction of a metal salt with a cyclic ligand under specific conditions. For example, the synthesis of ferrocene involves the reaction of cyclopentadienyl magnesium bromide with iron(II) chloride under an inert atmosphere. This method, known as the direct synthesis approach, is widely used for the preparation of various sandwich compounds.
Applications
Sandwich compounds have found applications in various fields, including:
- Catalysis: Many sandwich compounds, especially those containing transition metals, are used as catalysts in organic synthesis and industrial processes.
- Materials Science: Due to their unique electronic properties, some sandwich compounds are used in the development of organic semiconductors and other materials.
- Medicine: Certain sandwich compounds have shown potential in medical applications, including as anticancer agents.
Challenges and Future Directions
While sandwich compounds have been extensively studied, challenges remain in understanding their reactivity and expanding their applications. Future research may focus on developing new synthetic methods, exploring unsymmetrical sandwich compounds, and investigating their potential in emerging fields such as renewable energy and biotechnology.
See Also
- Small carborane sandwiches.png
Small carborane sandwiches
- Hexadecker.jpg
Hexadecker
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD