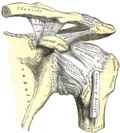
Superior transverse scapular ligament
Superior Transverse Scapular Ligament
The superior transverse scapular ligament is a small but important ligament located in the shoulder region. It is one of the ligaments that helps to stabilize the scapula (shoulder blade) and plays a crucial role in the movement and function of the shoulder joint.
Anatomy
The superior transverse scapular ligament is a thin, flat band of fibrous tissue that spans across the suprascapular notch, a small depression on the superior border of the scapula. It connects the medial (inner) border of the scapula to the lateral (outer) border, forming a bridge-like structure.
The ligament is approximately 2-3 centimeters in length and 1-2 millimeters in width. It is positioned superiorly to the suprascapular nerve, which passes beneath it. The suprascapular artery also runs above the ligament.
Function
The main function of the superior transverse scapular ligament is to create a protective tunnel for the suprascapular nerve as it passes through the suprascapular notch. This ligament prevents compression or impingement of the nerve, ensuring its proper functioning.
Additionally, the ligament provides stability to the scapula by connecting its medial and lateral borders. This stability is crucial for the proper movement and positioning of the scapula during shoulder movements.
Clinical Significance
Injuries or abnormalities related to the superior transverse scapular ligament can have significant clinical implications. If the ligament is damaged or torn, it can lead to compression or entrapment of the suprascapular nerve, resulting in suprascapular neuropathy. This condition can cause pain, weakness, and loss of function in the shoulder and upper arm.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing issues related to the superior transverse scapular ligament and suprascapular nerve can be challenging. A thorough physical examination, along with imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or ultrasound, may be necessary to identify any abnormalities.
Treatment options for injuries or conditions affecting the superior transverse scapular ligament and suprascapular nerve may include conservative measures such as rest, physical therapy, and pain management. In some cases, surgical intervention may be required to repair or release the ligament or decompress the nerve.
Related Topics
- Scapula: The shoulder blade bone to which the superior transverse scapular ligament is attached.
- Suprascapular Nerve: The nerve that passes beneath the superior transverse scapular ligament.
- Suprascapular Neuropathy: A condition caused by compression or entrapment of the suprascapular nerve.
- Shoulder Joint: The joint formed by the articulation of the scapula and the humerus.
References
1. Gray H. Anatomy of the Human Body. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1918. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563232/
2. Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2017.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD