Sympathetic ganglia
(Redirected from Sympathetic ganglion)
Sympathetic Ganglia
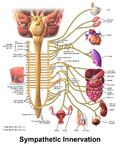
The sympathetic ganglia are a collection of nerve cell bodies (ganglia) situated in the sympathetic nervous system, a part of the autonomic nervous system. These ganglia are critical in the body's fight or flight response, regulating involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. The sympathetic ganglia are divided into two major chains: the paravertebral ganglia (or sympathetic chain ganglia) and the prevertebral ganglia.
Structure
The sympathetic ganglia are organized into two main groups: the paravertebral ganglia and the prevertebral ganglia.
Paravertebral Ganglia
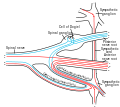
The paravertebral ganglia form a chain that runs alongside the vertebral column. This chain extends from the base of the skull to the coccyx, forming the sympathetic trunk. The paravertebral ganglia are connected to the spinal nerves through the rami communicantes, which contain both myelinated and unmyelinated fibers. These ganglia are primarily involved in the distribution of the sympathetic innervation to the body wall, head, neck, limbs, and thoracic cavity.
Prevertebral Ganglia
Prevertebral ganglia are located anterior to the vertebral column and close to the major abdominal arteries. They include the celiac, superior mesenteric, and inferior mesenteric ganglia. These ganglia primarily provide sympathetic innervation to the abdominal and pelvic viscera.
Function
The sympathetic ganglia play a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, preparing the body for physical activity by increasing heart rate, dilating bronchial passages, decreasing motility of the large intestine, constricting blood vessels, and causing pupil dilation. These actions are part of the body's fight or flight response to stress.
Clinical Significance
Abnormalities or damage to the sympathetic ganglia can lead to various disorders, including Horner's syndrome, which is characterized by ptosis (drooping eyelid), miosis (constricted pupil), and anhidrosis (lack of sweating) on the affected side of the face. Another condition, complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), involves severe chronic pain that can occur in an arm or leg after injury, surgery, stroke, or heart attack and is thought to be caused by dysfunctional sympathetic ganglia.
See Also
| Anatomy of the autonomic nervous system | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
This article is a neuroscience stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD