Theories of general anaesthetic action
Theories of General Anaesthetic Action
General anaesthetics are a class of drugs used in surgery to induce anesthesia, a state of unconsciousness, amnesia, analgesia, and immobility. The exact mechanisms by which these agents induce anesthesia are complex and not fully understood. However, several theories have been proposed to explain the action of general anaesthetics. This article explores the main theories of general anaesthetic action, including the lipid theory, the protein receptor theory, and the multi-site and multi-mechanism theory.
Lipid Theory
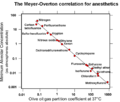
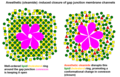
The lipid theory, one of the earliest hypotheses, suggests that general anaesthetics exert their effects by dissolving in the lipid bilayer of neuronal cell membranes, thereby disrupting the physical properties of the membrane. This disruption is thought to lead to a decrease in neuronal excitability. The theory was supported by the Meyer-Overton correlation, which observed a direct relationship between the potency of an anaesthetic and its solubility in olive oil, a model for cell membrane lipids. However, this theory could not explain the stereospecific effects of some anaesthetics, leading to the exploration of alternative theories.
Protein Receptor Theory
The protein receptor theory posits that general anaesthetics act by binding to specific protein targets in the nervous system, particularly ion channels. This interaction alters the function of these proteins, leading to changes in ion flow across the membrane and resulting in decreased neuronal excitability. Key targets include the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor, the glycine receptor, and the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. This theory is supported by the observation that many general anaesthetics have stereospecific effects, which suggests a specific molecular interaction with protein targets.
Multi-site and Multi-mechanism Theory
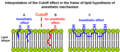
The multi-site and multi-mechanism theory combines elements of both the lipid and protein receptor theories. It proposes that general anaesthetics act through multiple mechanisms and at multiple sites, including both lipid membranes and protein receptors. This theory acknowledges the complexity of the central nervous system and the diverse chemical structures of general anaesthetics, suggesting that no single mechanism can fully explain their action. This approach has gained support as it accommodates the evidence for both lipid and protein receptor interactions and recognizes the variability in the effects of different anaesthetic agents.
Conclusion
The mechanisms of action of general anaesthetics are multifaceted and remain an area of active research. While the lipid theory and the protein receptor theory have provided foundational insights, the multi-site and multi-mechanism theory currently offers the most comprehensive explanation for the action of general anaesthetics. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for the development of safer and more effective anaesthetic agents.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD