Tree height measurement
Tree height measurement is the process of determining the height of trees, a key factor in forest management, timber estimation, and ecological studies. This measurement can be achieved through various methods, ranging from simple manual techniques to advanced technological tools.
Methods of Measurement
There are several methods for measuring the height of a tree, each with its own advantages and limitations.
Direct Measurement
Direct measurement involves physically measuring from the base of the tree to its highest point. This method is rarely used due to its impracticality, especially for tall trees.
Clinometer
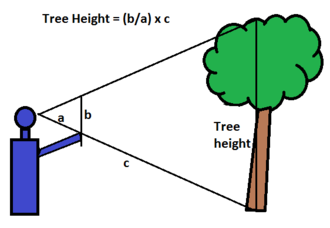
The most common method involves using a clinometer, an instrument that measures angles from a distance. By measuring the angle from the observer to the top of the tree and knowing the distance from the observer to the tree, trigonometry can calculate the tree's height.
Tangent Method
The tangent method is a simplified version that assumes the observer is at a right angle to the tree's base. It requires measuring the distance to the tree and the angle to the tree's top, using basic trigonometry to calculate height.
Sine Method
The sine method is considered more accurate than the tangent method, especially for steep angles. It uses the principle that the height of the tree is proportional to the sine of the angle to the top of the tree, requiring the same measurements as the tangent method but applying a different trigonometric function.
Laser Rangefinders
Laser rangefinders have become increasingly popular for tree height measurement. These devices calculate the distance to the tree and the angle to the top, using internal algorithms to compute the tree's height accurately.
Drones
Drones equipped with GPS and imaging technology can also be used to measure tree heights. They offer a bird's-eye view, allowing for precise measurements of even the tallest trees without the need for direct access.
Applications
Tree height measurement is crucial in various fields:
- In forestry, it helps in estimating timber volume and managing forests sustainably.
- In ecology, tree height is used to assess habitat characteristics and biodiversity.
- In urban planning, understanding tree heights can aid in designing landscapes and managing urban forests.
Challenges
Measuring the height of trees presents several challenges, including:
- Accessibility of the tree, especially in dense forests or rugged terrain.
- Accuracy of the measurement tools and methods, particularly for very tall or oddly shaped trees.
- Environmental conditions, such as wind or light, can affect the accuracy of measurements.
Conclusion
Tree height measurement is a vital practice in forestry, ecology, and urban planning. Despite the challenges, advancements in technology have made it easier and more accurate to measure the height of trees, contributing to better management and conservation of forest resources.
| This article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by registering to expand it. |
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD