Tympanic cavity
Anatomical cavity in the ear
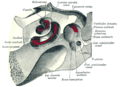
The tympanic cavity is a small, air-filled space located in the temporal bone of the skull. It is part of the middle ear and plays a crucial role in the process of hearing by transmitting sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear.
Anatomy
The tympanic cavity is bounded laterally by the tympanic membrane (eardrum) and medially by the bony labyrinth of the inner ear. It is connected to the nasopharynx via the Eustachian tube, which helps equalize pressure between the middle ear and the atmosphere.
Walls
The tympanic cavity has six walls:
- Lateral wall: Formed by the tympanic membrane.
- Medial wall: Contains the oval window and round window, which are openings into the inner ear.
- Anterior wall: Contains the opening of the Eustachian tube and the canal for the tensor tympani muscle.
- Posterior wall: Contains the entrance to the mastoid antrum and the pyramidal eminence.
- Roof: Formed by a thin plate of bone called the tegmen tympani.
- Floor: Formed by the jugular wall, which separates the tympanic cavity from the jugular fossa.
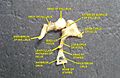
Contents
The tympanic cavity contains three small bones known as the ossicles: the malleus, incus, and stapes. These bones form a chain that transmits sound vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the oval window of the inner ear.
Function
The primary function of the tympanic cavity is to facilitate the transmission of sound from the external ear to the inner ear. The ossicles amplify and convey sound vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the oval window, where they are converted into fluid waves in the cochlea of the inner ear.
Clinical significance
Conditions affecting the tympanic cavity include otitis media, which is an infection or inflammation of the middle ear, and otosclerosis, a condition that affects the movement of the stapes bone. Proper functioning of the Eustachian tube is essential for maintaining equal air pressure on both sides of the tympanic membrane.
Images
Related pages
References
- Moore, K. L., Dalley, A. F., & Agur, A. M. R. (2013). Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Standring, S. (2015). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD