Union (American Civil War)
File:Four Ruffles and Flourishes and Hail Columbia.ogg}}<br_/>|right|thumb|Four_Ruffles_and_Flourishes_and_Hail_Columbia.ogg]]}}<br_/>]] File:Rufst du, mein Vaterland (1938).oga}}|right|thumb|Rufst_du,_mein_Vaterland,_God_Save_the_King,_Íslands_minni,_Kongesangen_and_Oben_am_jungen_Rhein_(1938).oga]]}}]]
== Union (American Civil War) ==
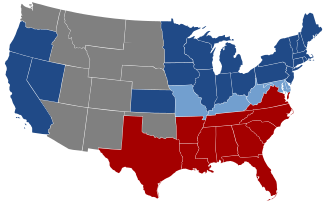
The Union refers to the United States of America and specifically to the national government and the 20 free states and 5 border states that supported it during the American Civil War. It was opposed by the Confederate States of America, commonly referred to as the Confederacy, which was composed of 11 Southern slave states that had declared their secession from the United States.
Background
The Union was led by President Abraham Lincoln and the Republican Party, which was founded on anti-slavery principles. The conflict began in April 1861 when Confederate forces attacked Fort Sumter in South Carolina, prompting Lincoln to call for volunteers to suppress the rebellion.
Military Structure
The Union's military forces were known as the Union Army and the Union Navy. The Union Army was composed of both regular army units and volunteer regiments raised by the states. Key military leaders included Ulysses S. Grant, William Tecumseh Sherman, and George McClellan.
Economy and Resources
The Union had a significant advantage in terms of industrial capacity, infrastructure, and population. The Northern states were more industrialized and had a more extensive railway network, which facilitated the movement of troops and supplies. The Union also had a more substantial financial system and access to international trade.
Key Battles
Some of the major battles involving Union forces included the Battle of Gettysburg, the Battle of Antietam, and the Siege of Vicksburg. The Union's victory at Gettysburg in July 1863 and the capture of Vicksburg shortly thereafter were turning points in the war.
Emancipation Proclamation
In January 1863, President Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation, which declared that all slaves in Confederate-held territory were to be set free. This shifted the war aims of the Union to include the abolition of slavery, in addition to preserving the Union.
End of the War
The Civil War ended in April 1865 with the surrender of Confederate General Robert E. Lee at Appomattox Court House. The Union's victory led to the preservation of the United States as a single nation and the abolition of slavery.
Reconstruction
Following the war, the Union entered a period known as Reconstruction, during which the Southern states were gradually readmitted to the Union, and efforts were made to integrate formerly enslaved people into American society.
Related Pages
- American Civil War
- Confederate States of America
- Abraham Lincoln
- Union Army
- Union Navy
- Emancipation Proclamation
- Reconstruction era
Categories
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD