Ustilaginomycotina
A subphylum of fungi in the phylum Basidiomycota
Ustilaginomycotina is a subphylum of fungi within the phylum Basidiomycota. This group is primarily composed of smut fungi, which are known for their parasitic relationship with plants, particularly grasses. The subphylum includes several important plant pathogens that affect agricultural crops.
Taxonomy
Ustilaginomycotina was established as a subphylum in 2006 by Bauer and colleagues. It is one of the three subphyla of Basidiomycota, the others being Agaricomycotina and Pucciniomycotina. The subphylum is divided into three classes: Ustilaginomycetes, Exobasidiomycetes, and Malasseziomycetes.
Classes
- Ustilaginomycetes: This class includes the majority of the smut fungi, which are characterized by their production of teliospores. The most well-known member is Ustilago maydis, the causative agent of corn smut.
- Exobasidiomycetes: Members of this class are also plant pathogens, but they have a different life cycle and morphology compared to Ustilaginomycetes.
- Malasseziomycetes: This class includes fungi that are primarily associated with animals, particularly mammals, and are known for causing skin conditions.
Life Cycle
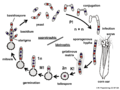
The life cycle of Ustilaginomycotina fungi typically involves both asexual and sexual reproduction. In the case of Ustilago maydis, the fungus infects the host plant, Zea mays (corn), and induces the formation of galls. These galls contain the teliospores, which are the resting spores of the fungus. Upon germination, the teliospores undergo meiosis to produce basidiospores, which can infect new host plants.
Ecological and Economic Importance
Ustilaginomycotina fungi are significant both ecologically and economically. They play a role in the decomposition of organic matter and nutrient cycling. However, as plant pathogens, they can cause substantial damage to crops, leading to economic losses. The study of these fungi is important for developing strategies to control plant diseases and improve crop yields.
Related pages
References
- Bauer, R., Begerow, D., Sampaio, J.P., Weiss, M., & Oberwinkler, F. (2006). The classification of Basidiomycota. In: The Mycota VII Part A. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
- Piepenbring, M. (2007). Life cycle of Ustilago maydis on corn, Ustilaginales Basidiomycota. [Image].
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD