Wood-decay fungus
Wood-decay fungus is a type of fungus that digests moist wood, causing it to rot. Some species of wood-decay fungi attack dead wood, such as brown rot, and some, such as Armillaria (Honey fungus), are parasitic and colonize living trees. Excessive moisture above the fibre saturation point in wood is required for fungal colonization and proliferation.
Types of Wood-decay Fungus
Wood-decay fungi can be classified according to the type of decay that they cause. The best-known types are brown rot, soft rot, and white rot.
Brown Rot
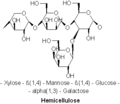
Brown rot fungi break down hemicellulose and cellulose that form the wood structure. Cellulose is broken down by hydrogen peroxide that is produced during the breakdown of hemicellulose. Because of this simultaneous breakdown of cellulose and hemicellulose, the wood shrinks, shows a brown discoloration, and cracks into rectangular pieces, a phenomenon termed cubical fracture.
Soft Rot
Soft rot fungi secrete cellulase from their hyphae, an enzyme that breaks down cellulose in the wood. This leads to the formation of microscopic cavities inside the wood, and the wood becomes spongy to the touch.
White Rot
White rot fungi break down the lignin in wood, leaving the lighter-colored cellulose behind. Some white rots break down both lignin and cellulose. White rot may give the wood a bleached appearance and often takes longer to develop than brown rot.
Ecology
Wood-decay fungi play a very significant role in the carbon cycle. By breaking down the wood they are able to return nutrients back into the soil from where new plants can absorb them. They also use the carbon in the wood as a source of energy, which they then release back into the ecosystem as carbon dioxide.
Economic Impact
Wood-decay fungi can cause significant damage to wooden structures, furniture, and other items made of wood. They can also be a problem in forests, where they can cause the death of trees. However, they also play an important role in the decomposition of wood in nature, which is beneficial for the recycling of nutrients.
See Also
This article is a Decomposition-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD