Acute limb ischaemia
| Acute limb ischaemia | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Pain, pallor, pulselessness, paresthesia, paralysis, poikilothermia |
| Complications | Tissue necrosis, gangrene, amputation |
| Onset | Sudden |
| Duration | Hours to days |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Embolism, thrombosis, trauma |
| Risks | Atrial fibrillation, peripheral artery disease, smoking, diabetes mellitus |
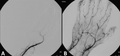
| Diagnosis | Doppler ultrasound, angiography |
| Differential diagnosis | Deep vein thrombosis, compartment syndrome |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Anticoagulation, thrombolysis, surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on time to treatment |
| Frequency | Common in patients with cardiovascular disease |
| Deaths | N/A |
Acute Limb Ischaemia
Acute limb ischaemia (ALI) is a sudden decrease in blood flow to a limb, threatening its viability. It is a medical emergency that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent tissue necrosis and potential amputation.
Causes
Acute limb ischaemia can result from several causes, including:
- Embolism: A blood clot or other debris travels through the bloodstream and lodges in a limb artery.
- Thrombosis: A blood clot forms in a limb artery, often due to underlying atherosclerosis.
- Trauma: Physical injury to a limb can damage blood vessels, leading to ischaemia.
- Aortic dissection: A tear in the aorta can extend into limb arteries, reducing blood flow.
Symptoms
The classic symptoms of acute limb ischaemia are often referred to as the "six Ps":
- Pain
- Pallor
- Pulselessness
- Paresthesia
- Paralysis
- Poikilothermia (coolness)
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of acute limb ischaemia involves a combination of clinical assessment and imaging studies. Common diagnostic tools include:
- Doppler ultrasound: To assess blood flow in the affected limb.
- Angiography: Provides detailed images of blood vessels to identify blockages.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) angiography: Non-invasive imaging techniques to visualize blood vessels.
Treatment
The treatment of acute limb ischaemia aims to restore blood flow and prevent tissue damage. Options include:
- Thrombolysis: Administration of drugs to dissolve blood clots.
- Surgical embolectomy: Removal of the embolus or thrombus through surgery.
- Bypass surgery: Creating a new pathway for blood flow around the blocked artery.
- Amputation: In severe cases where tissue death has occurred, amputation may be necessary.
Prognosis
The prognosis of acute limb ischaemia depends on the severity and duration of the ischaemia, as well as the underlying cause. Prompt treatment can significantly improve outcomes and limb salvage rates.
Prevention
Preventive measures focus on managing risk factors for vascular disease, such as:
Related pages
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD