Adenosine deaminase 2 deficiency
| Adenosine deaminase 2 deficiency | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | DADA2, Deficiency of ADA2 |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Rheumatology, Immunology, Hematology |
| Symptoms | Fever, Stroke, Vasculitis, Immunodeficiency, Cytopenia |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Childhood |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Mutations in the CECR1 gene |
| Risks | Family history of the condition |
| Diagnosis | Genetic testing, Clinical evaluation |
| Differential diagnosis | Polyarteritis nodosa, Systemic lupus erythematosus, Juvenile idiopathic arthritis |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Immunosuppressive therapy, Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depending on severity and treatment |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Adenosine deaminase 2 deficiency
A rare genetic disorder affecting the immune system
Adenosine deaminase 2 deficiency (DADA2) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by a deficiency in the enzyme adenosine deaminase 2 (ADA2). This condition primarily affects the immune system, leading to a range of symptoms including vasculitis, immunodeficiency, and hematological abnormalities.
Genetics
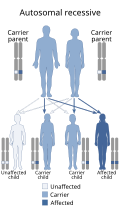
DADA2 is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning that an individual must inherit two copies of the defective gene, one from each parent, to manifest the disease. The gene responsible for DADA2 is the CECR1 gene, which encodes the ADA2 enzyme. Mutations in this gene lead to reduced or absent activity of ADA2, resulting in the clinical manifestations of the disorder.
Pathophysiology
The ADA2 enzyme is involved in the breakdown of adenosine and deoxyadenosine, which are important for normal immune function. Deficiency in ADA2 leads to the accumulation of these substrates, causing immune dysregulation and inflammation. The exact mechanisms by which ADA2 deficiency leads to the diverse symptoms observed in DADA2 are still under investigation.
Clinical Features
Patients with DADA2 may present with a variety of symptoms, including:
- Vasculitis, particularly affecting small and medium-sized blood vessels
- Strokes, often occurring in childhood
- Fever
- Rash
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Anemia and other blood cell abnormalities
- Immunodeficiency, leading to increased susceptibility to infections
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of DADA2 is based on clinical evaluation, laboratory findings, and genetic testing. Measurement of ADA2 enzyme activity in the blood can support the diagnosis, but genetic testing for mutations in the CECR1 gene is definitive.
Treatment
There is no cure for DADA2, but treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. Immunosuppressive therapy may be used to control inflammation, and anti-TNF therapy has shown effectiveness in some patients. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation may be considered in severe cases.
Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with DADA2 varies depending on the severity of the symptoms and the effectiveness of treatment. Early diagnosis and management are crucial for improving outcomes.
Related pages
Gallery
Adenosine deaminase 2 deficiency
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD