Altrose
Altrose
Altrose is a type of monosaccharide, specifically an aldohexose, which means it is a six-carbon sugar with an aldehyde group. It is one of the rare sugars and is not commonly found in nature. Altrose is an epimer of allose, differing in the configuration around one specific carbon atom.
Structure
Altrose has the chemical formula C_H__O_. It is a stereoisomer of glucose, meaning it has the same molecular formula but a different three-dimensional arrangement of atoms. The structure of altrose can be represented in both its open-chain form and its cyclic form. In the open-chain form, altrose has an aldehyde group at the first carbon, and hydroxyl groups attached to the other carbons.
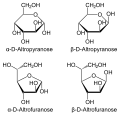
In its cyclic form, altrose can form a six-membered ring called a pyranose. The cyclic form is more stable and is the predominant form in aqueous solutions. The specific configuration of altrose is determined by the orientation of the hydroxyl groups on the asymmetric carbon atoms.
Stereochemistry
Altrose is one of the eight D-aldohexoses, which also include glucose, mannose, galactose, gulose, idose, talose, and allose. The D- and L- configurations refer to the orientation of the hydroxyl group on the chiral carbon farthest from the aldehyde group. D-altrose is the enantiomer of L-altrose.
Biological Role
Altrose is not commonly found in nature and does not play a significant role in biological systems. It is not a major component of any known metabolic pathways in humans or other organisms. However, like other rare sugars, altrose can be synthesized in the laboratory and studied for its potential applications in medicine and biotechnology.
Synthesis
Altrose can be synthesized through various chemical methods, including the Kiliani-Fischer synthesis, which involves the chain extension of an aldose sugar. It can also be produced through the epimerization of other sugars, such as allose, using specific enzymes or chemical catalysts.
Applications
While altrose itself is not widely used, the study of rare sugars like altrose is important in the field of carbohydrate chemistry. Understanding the properties and reactions of these sugars can lead to the development of new pharmaceuticals and other biotechnological applications.
Related pages
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD