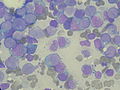
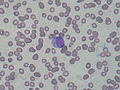
Auer rod
Auer rods—also known as Auer bodies—are distinctive, crystalline cytoplasmic inclusion bodies that can be identified in the myeloid blast cells of certain hematological diseases. Their presence is particularly associated with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), as well as high-grade Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Myeloproliferative Disorders.
Composition and Structure
Auer rods are composed of fused lysosomes and are rich in lysosomal enzymes. They are azurophilic, meaning they stain readily with the Romanowsky type dyes due to their affinity for acidic dyes like eosin. Morphologically, Auer rods can resemble various shapes such as needles, commas, diamonds, rectangles, corkscrews, or, though rarely, granules.
Pathophysiology
The formation of Auer rods is not fully understood, but they are considered to be a byproduct of abnormal myeloid cell development and differentiation seen in certain hematologic malignancies. They are abnormal accumulations of peroxidase-positive material, such as Myeloperoxidase, that are typically not found in normal leukocytes.
Clinical Significance
The presence of Auer rods in myeloid precursors is a pathognomonic sign of a pathological process and is critical in the diagnosis of certain types of leukemia. Their detection often involves a bone marrow examination and cytochemical staining, and is an important criterion in the French-American-British (FAB) Classification system used to classify AML.
Associated Conditions
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
- High-grade Myelodysplastic syndromes
- Myeloproliferative disorders
Detection and Examination
Auer rods are detected through microscopic examination of blood or bone marrow samples. They are especially visible under light microscopy in cells stained with Romanowsky stains, such as Wright's or Giemsa stain. In some cases, they may be seen in peripheral blood smears, but they are more commonly found during bone marrow analysis.
Prognostic Value
In some types of leukemia, the presence of Auer rods may have prognostic implications, aiding in risk stratification and treatment planning.
In Medical Education
The identification of Auer rods is a key component of medical education in Hematology and Pathology, training healthcare professionals to recognize important diagnostic features of hematological disorders.
Gallery
Bone marrow aspirate showing acute myeloid leukemia with Auer rods in several blasts
| This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it! | |
|---|---|
| Abnormal clinical and laboratory findings for blood tests (ICD-10 R70–R79, ICD-9 780–799) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD