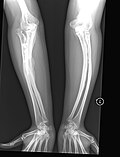
Osteogenesis imperfecta
(Redirected from Brittle bone disease)
| Osteogenesis imperfecta | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Brittle bone disease, Lobstein syndrome |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Field | Pediatrics, medical genetics, osteology |
| Symptoms | Bones that break easily, blue tinge to the whites of the eye, short height, loose joints, hearing loss |
| Complications | |
| Onset | |
| Duration | Long term |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic (autosomal dominant, new mutation) |
| Risks | |
| Diagnosis | Based on symptoms, DNA testing |
| Differential diagnosis | |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Healthy lifestyle (exercise, no smoking), metal rods through the long bones |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Depends on the type |
| Frequency | 1 in 15,000 people |
| Deaths | |
Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI), commonly known as brittle bone disease, is a spectrum of genetic disorders primarily affecting the bones, leading to increased fragility and susceptibility to fractures.
Introduction
OI is characterized by bones that break easily, often with no apparent cause. The condition can range in severity from mild to severe, and can affect individuals differently, even within the same family.
Clinical Presentation
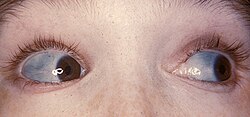
People with OI might have a blue tinge to the whites of the eyes (sclera), short height, loose joints, and hearing loss. The disease can also cause respiratory issues due to weak respiratory muscles and a restrictive lung disease pattern. Dental abnormalities, often termed "dentinogenesis imperfecta," can lead to discolored, brittle teeth that are prone to cavities.
Genetics
OI is caused by mutations in the genes that produce collagen, a protein crucial for bone strength. Most cases of OI are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning that an affected person has a 50% chance of passing the disorder to each of their children.
Treatment and Management
There's currently no cure for OI, but the symptoms can be managed to help individuals with OI maintain their independence. Treatments may include physical therapy, surgery, medications, and lifestyle modifications.
Complications
Possible complications of OI include cervical artery dissection and aortic dissection, which are serious conditions requiring immediate medical attention.
Epidemiology
OI affects approximately 1 in 20,000 people, making it a rare disorder. It affects both males and females of all ethnic backgrounds.
See Also
| This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it! | |
|---|---|
| Diseases of collagen, laminin and other scleroproteins | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
see also fibrous proteins
|
| Osteochondrodysplasias | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD