Ciliopathy
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Ciliopathy | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Kidney disease, retinal degeneration, liver fibrosis, cognitive impairment |
| Complications | Organ failure, blindness, infertility |
| Onset | Varies by specific condition |
| Duration | Chronic |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic mutations affecting cilia |
| Risks | Family history of ciliopathies |
| Diagnosis | Genetic testing, imaging studies |
| Differential diagnosis | Polycystic kidney disease, Bardet-Biedl syndrome, Alström syndrome |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Symptomatic management, organ transplantation |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Varies depending on specific condition and severity |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
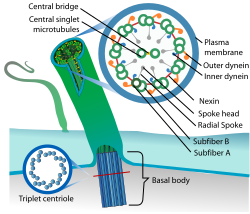
Ciliopathy is a group of genetic disorders caused by the dysfunction of cilia, which are hair-like structures present on the surface of most eukaryotic cells. These disorders can affect multiple organ systems and lead to a wide range of clinical manifestations.
Structure and Function of Cilia
Cilia are classified into two main types: motile cilia and primary cilia. Motile cilia are involved in movement, such as the clearing of mucus in the respiratory tract, while primary cilia function as sensory organelles, playing a crucial role in signal transduction pathways.
Genetics
Ciliopathies are typically inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, although some can be autosomal dominant. Mutations in genes encoding proteins that are part of the ciliary structure or its associated machinery can lead to ciliopathies. Some of the genes commonly associated with ciliopathies include PKD1, PKD2, and IFT88.
Clinical Manifestations
Ciliopathies can present with a wide range of symptoms, depending on the organs affected. Common clinical features include:
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Retinal degeneration
- Liver fibrosis
- Obesity
- Skeletal abnormalities
- Intellectual disability
Types of Ciliopathies
Several specific disorders fall under the umbrella of ciliopathies, including:
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Bardet-Biedl syndrome
- Joubert syndrome
- Meckel-Gruber syndrome
- Nephronophthisis
- Alström syndrome
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of ciliopathies often involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and genetic testing. Ultrasound and MRI can be used to identify structural abnormalities in organs such as the kidneys and liver. Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis by identifying mutations in cilia-related genes.
Treatment
There is currently no cure for ciliopathies, and treatment is primarily supportive and symptomatic. Management strategies may include:
- Dialysis or kidney transplantation for renal failure
- Physical therapy and occupational therapy for motor and developmental delays
- Surgical interventions for structural abnormalities
Research
Ongoing research aims to better understand the molecular mechanisms underlying ciliopathies and to develop targeted therapies. Advances in gene therapy and stem cell research hold promise for future treatment options.
See Also
References
External Links
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD


