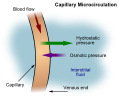
Extracellular fluid
Extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. In humans, this includes the blood plasma, interstitial fluid, lymph and cerebrospinal fluid. The extracellular fluid also includes the transcellular fluid, which comprises of fluid contained in special body spaces, such as the synovial fluid in joints, the pleural fluid in the pleural cavities, the pericardial fluid in the cardiac sac, the intraocular fluid in the eyes, and the cerebrospinal fluid in the brain and spine.
Composition
The extracellular fluid is essentially an aqueous solution containing a variety of substances, including electrolytes, glucose, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. The electrolytes in the ECF are primarily sodium, chloride, and bicarbonate, with smaller amounts of potassium, calcium, and magnesium. The ECF also contains larger molecules such as proteins and other organic and inorganic compounds.
Function
The primary function of the extracellular fluid is to provide a consistent environment for the body's cells. It allows for the exchange of nutrients and waste products between the cells and the blood, and helps to maintain the acid-base balance in the body. The ECF also plays a crucial role in the body's immune response, as it contains the white blood cells that fight off infections.
Regulation
The volume and composition of the extracellular fluid are tightly regulated by a variety of mechanisms, including the kidneys, which filter the blood and excrete excess water and electrolytes in the urine. The lungs also play a role in regulating the ECF, as they remove carbon dioxide (a waste product of cellular metabolism) from the body and help to maintain the acid-base balance.
Disorders
Disorders of the extracellular fluid can occur when there is an imbalance in the volume or composition of the ECF. This can result from a variety of conditions, including kidney disease, heart failure, and liver disease. Symptoms of ECF disorders can include edema (swelling), dehydration, and changes in blood pressure.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD