Geology
Study of the Earth and its processes
Geology is the scientific study of the Earth, including its composition, structure, physical properties, and history. It is a major branch of the Earth sciences and encompasses the study of the solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Geology provides insights into the Earth's past, including the evolution of life and past climates, and helps predict future geological events and changes.
Branches of Geology
Geology is a broad field that includes several sub-disciplines:
- Petrology: The study of rocks and the conditions under which they form.
- Mineralogy: The study of minerals, their structure, properties, and classification.
- Paleontology: The study of fossils and ancient life forms.
- Sedimentology: The study of sedimentary rocks and the processes of sedimentation.
- Structural geology: The study of rock formations and the forces that shape them.
- Volcanology: The study of volcanoes and volcanic phenomena.
- Seismology: The study of earthquakes and the propagation of seismic waves.
Geological Processes
Geological processes are dynamic and shape the Earth's surface over time. These include:
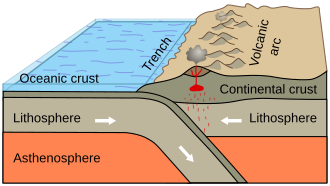
- Plate tectonics: The movement of the Earth's lithospheric plates that leads to the formation of mountains, earthquakes, and volcanic activity.
- Erosion and weathering: The processes that break down rocks and transport sediments.
- Sedimentation: The deposition of sediments in layers, forming sedimentary rocks.
- Metamorphism: The alteration of rocks by heat, pressure, and chemical processes.
- Volcanism: The eruption of magma onto the Earth's surface, forming volcanic rocks.
The Rock Cycle
The rock cycle is a fundamental concept in geology that describes the transformation of rocks through various geological processes. It involves the formation, breakdown, and reformation of rocks.
- Igneous rocks form from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
- Sedimentary rocks form from the accumulation and lithification of sediments.
- Metamorphic rocks form from the alteration of existing rocks under heat and pressure.
Geological Time
Geological time is a system of chronological dating that relates geological strata to time. It is used by geologists to describe the timing and relationships of events in Earth's history. The geological time scale is divided into eons, eras, periods, epochs, and ages.
Applications of Geology
Geology has numerous practical applications, including:
- Natural resource exploration: Locating and extracting minerals, oil, and gas.
- Environmental geology: Assessing and mitigating environmental impacts of human activities.
- Engineering geology: Providing geological information for construction and infrastructure projects.
- Hazard assessment: Predicting and mitigating natural disasters such as earthquakes, landslides, and volcanic eruptions.
Related Pages
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD