Lateralization of brain function
Lateralization of brain function refers to the phenomenon wherein one hemisphere of the brain is more adept or responsible for certain functions than the other. This concept is a crucial aspect of neuroscience and psychology, as it helps explain the complex nature of brain functionality and human behavior.
Overview
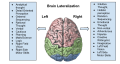
The human brain is divided into two hemispheres: the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere. Each hemisphere is responsible for controlling the opposite side of the body. However, the two hemispheres are not identical and have different specializations, a concept known as lateralization of brain function.
Left Hemisphere
The left hemisphere is traditionally associated with analytical and logical processes, including language, mathematics, and reasoning. It is also involved in controlling the right side of the body.
Language
The left hemisphere is predominantly responsible for language abilities in most right-handed individuals and a significant number of left-handed individuals. Key language areas located in the left hemisphere include Broca's area and Wernicke's area, which are involved in speech production and comprehension, respectively.
Analytical Abilities
The left hemisphere is also associated with analytical abilities, such as mathematical computations and logical reasoning. It processes information in a linear and sequential manner, allowing for detailed analysis of situations.
Right Hemisphere
The right hemisphere is traditionally associated with creative and intuitive processes, including spatial abilities, face recognition, and music appreciation. It is also involved in controlling the left side of the body.
Spatial Abilities
The right hemisphere plays a significant role in spatial abilities, such as navigating through space and recognizing faces. It processes information in a holistic and simultaneous manner, allowing for a broad understanding of situations.
Creative Abilities
The right hemisphere is also associated with creative abilities, such as music appreciation and artistic abilities. It is thought to be more involved in the processing of visual imagery and the interpretation of contexts.
Lateralization and Handedness
The lateralization of brain function is also linked to handedness. Most right-handed individuals have left-hemisphere dominance for language, while left-handed individuals may have either left or right hemisphere dominance for language.
See Also
References
This article is a neuroscience stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
This article is a psychology-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD