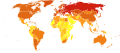
List of countries by risk of death from non-communicable disease
List of Countries by Risk of Death from Non-Communicable Disease is a comprehensive enumeration that ranks countries based on the probability of mortality attributed to non-communicable diseases (NCDs). NCDs, also known as chronic diseases, are not passed from person to person and have a long duration and generally slow progression. The four main types of non-communicable diseases include cardiovascular diseases, cancer, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes mellitus.
Overview
Non-communicable diseases are the leading cause of death globally, representing a major public health challenge that all countries face. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), NCDs kill 41 million people each year, equivalent to 71% of all deaths globally. These diseases disproportionately affect people in low- and middle-income countries, where more than three-quarters of global NCD deaths occur.
The risk of death from NCDs is calculated based on a variety of factors, including but not limited to, the prevalence of tobacco use, unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, and the harmful use of alcohol. Other determinants include socioeconomic factors, genetics, and environmental exposures.
Ranking
The list of countries by risk of death from non-communicable disease is updated periodically by the World Health Organization and other international health bodies. The rankings are determined through the analysis of health data, including mortality rates and the prevalence of risk factors associated with NCDs.
Countries with the highest risk of death from NCDs often have inadequate healthcare systems, poor health education, and limited access to preventive measures. Conversely, countries with the lowest risk typically have robust healthcare systems, widespread health education, and effective policies for reducing risk factors.
Prevention and Control
Preventing and controlling non-communicable diseases involves a comprehensive approach that includes policy interventions, public health campaigns, and individual actions. Strategies to reduce the risk of NCDs include:
- Promoting a healthy diet and physical activity
- Reducing tobacco and alcohol use
- Improving access to quality healthcare
- Implementing policies to reduce air pollution and environmental risks
- Enhancing awareness and education on the risks of NCDs
Conclusion
The list of countries by risk of death from non-communicable disease highlights the global impact of chronic diseases and the importance of concerted efforts to reduce their prevalence. By understanding the factors that contribute to the high risk of NCDs, countries can implement targeted interventions to improve public health and reduce the burden of these diseases.
This article is a Public health stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
List of countries by risk of death from non-communicable disease
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD