Nerve
(Redirected from Nerves)
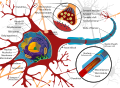
A nerve contains bundles of nerve fibers, either axons or dendrites, surrounded by connective tissue.
Types of nerves
- Sensory nerves contain only afferent fibers, long dendrites of sensory neurons.
- Motor nerves have only efferent fibers, long axons of motor neurons.
- Mixed nerves contain both types of fibers.
Epineurium
A connective tissue sheath called the epineurium surrounds each nerve. Each bundle of nerve fibers is called a fasciculus and is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Within the fasciculus, each individual nerve fiber, with its myelin and neurilemma, is surrounded by connective tissue called the endoneurium. A nerve may also have blood vessels enclosed in its connective tissue wrappings.
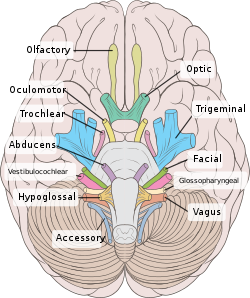
Cranial Nerves
Twelve pairs of cranial nerves emerge from the inferior surface of the brain. All of these nerves, except the [glossary term:] vagus nerve, pass through foramina of the skull to innervate structures in the head, neck, and facial region.
The cranial nerves are designated both by name and by Roman numerals, according to the order in which they appear on the inferior surface of the brain. Most of the nerves have both sensory and motor components. Three of the nerves are associated with the special senses of smell, vision, hearing, and equilibrium and have only sensory fibers. Five other nerves are primarily motor in function but do have some sensory fibers for proprioception. The remaining four nerves consist of significant amounts of both sensory and motor fibers.
Neuromas
Acoustic neuromas are benign fibrous growths that arise from the balance nerve, also called the eighth cranial nerve or vestibulocochlear nerve. These tumors are non-malignant, meaning that they do not spread or metastasize to other parts of the body. The location of these tumors is deep inside the skull, adjacent to vital brain centers in the brain stem. As the tumors enlarge, they involve surrounding structures which have to do with vital functions. In the majority of cases, these tumors grow slowly over a period of years. In other cases, the growth rate is more rapid and patients develop symptoms at a faster pace. Usually, the symptoms are mild and many patients are not diagnosed until some time after their tumor has developed. Many patients also exhibit no tumor growth over a number of years when followed by yearly MRI scans.
Spinal Nerves
Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves emerge laterally from the spinal cord. Each pair of nerves corresponds to a segment of the cord and they are named accordingly. This means there are 8 cervical nerves, 12 thoracic nerves, 5 lumbar nerves, 5 sacral nerves, and 1 coccygeal nerve.
Each spinal nerve is connected to the spinal cord by a dorsal root and a ventral root. The cell bodies of the sensory neurons are in the dorsal root ganglion, but the motor neuron cell bodies are in the gray matter. The two roots join to form the spinal nerve just before the nerve leaves the vertebral column. Because all spinal nerves have both sensory and motor components, they are all mixed nerves.
Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system is a visceral efferent system, which means it sends motor impulses to the visceral organs. It functions automatically and continuously, without conscious effort, to innervate smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands. It is concerned with heart rate, breathing rate, blood pressure, body temperature, and other visceral activities that work together to maintain homeostasis.
The autonomic nervous system has two parts, the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division. Many visceral organs are supplied with fibers from both divisions. In this case, one stimulates and the other inhibits. This antagonistic functional relationship serves as a balance to help maintain homeostasis.
Also see Nervous system
| This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it! | |
|---|---|
| Human systems and organs | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Spinal nerves | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| The cranial nerves | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Nerves of the cervical plexus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Nerve supply of the human arm | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Anatomy of the autonomic nervous system | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Nerves of the lumbosacral plexus | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD