Nerve injury
(Redirected from Peripheral nerve injury)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Nerve injury | |
|---|---|

| |
| Synonyms | Peripheral nerve injury, neuropathy |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, pain |
| Complications | Chronic pain, muscle atrophy, loss of function |
| Onset | Acute or chronic |
| Duration | Varies depending on severity and treatment |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Trauma, compression, ischemia, inflammation |
| Risks | Diabetes, alcoholism, autoimmune disorders |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, nerve conduction study, electromyography |
| Differential diagnosis | Radiculopathy, myopathy, central nervous system disorders |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, medication, surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on cause and severity |
| Frequency | Common |
| Deaths | N/A |
Nerve fascicle is a bundle of nerve fibers, enclosed by a layer of connective tissue known as the perineurium. It is a component of a nerve, along with other fascicles and additional layers of connective tissue.
Structure
Each nerve fascicle contains many nerve fibers. These fibers are long, slender projections of neurons, sometimes referred to as axons or nerve cells. They transmit electrical impulses from one area of the body to another. The nerve fibers within a fascicle are surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. This layer provides a supportive framework for the nerve fibers, helping to maintain their structure and function. The fascicle itself is enclosed by another layer of connective tissue, the perineurium. This layer helps to protect the nerve fibers from damage and infection. It also helps to maintain the integrity of the nerve, ensuring that the electrical impulses are transmitted efficiently.
Function
The primary function of a nerve fascicle is to transmit electrical impulses along the nerve fibers. These impulses carry information from one part of the body to another, enabling us to sense and respond to our environment. For example, when you touch a hot surface, nerve fibers in your skin transmit an impulse to your brain, which interprets this as pain and triggers a response to pull your hand away. This entire process is facilitated by the structure and function of nerve fascicles.
Clinical significance
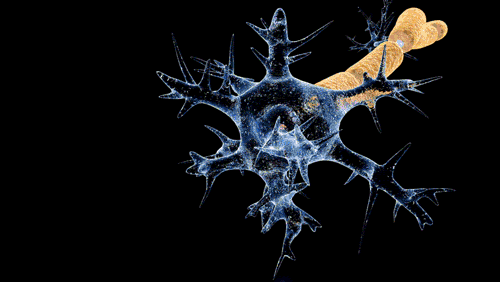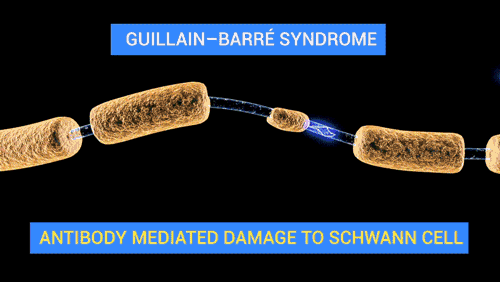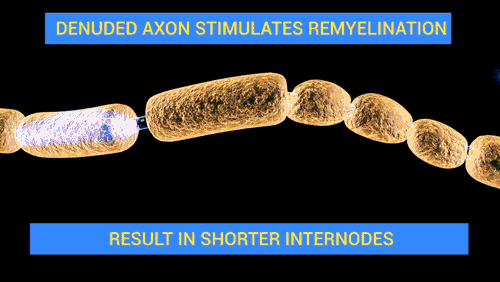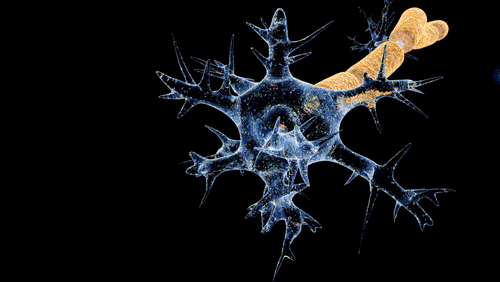
Damage or disease affecting the nerve fascicles can lead to a range of neurological disorders. For example, peripheral neuropathy is a condition in which the peripheral nerves, including the fascicles, are damaged, leading to symptoms such as pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected areas. Guillain-Barré syndrome is another condition that can affect the nerve fascicles. This is an autoimmune disorder in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the nerves, leading to weakness and numbness.
See also
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD