Peripheral edema
(Redirected from Peripheral oedema)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Peripheral edema | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Peripheral oedema, leg swelling |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
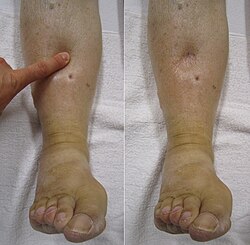
| Symptoms | Swelling of the lower limbs, ankles, and feet |
| Complications | Skin ulcer, infection, pain |
| Onset | Gradual |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Heart failure, kidney disease, liver cirrhosis, venous insufficiency, lymphatic obstruction |
| Risks | Obesity, pregnancy, prolonged standing, sedentary lifestyle |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, medical history, ultrasound, blood tests |
| Differential diagnosis | Deep vein thrombosis, cellulitis, lipedema |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Diuretics, compression stockings, elevation of legs, exercise |
| Medication | Furosemide, spironolactone |
| Prognosis | Depends on underlying cause |
| Frequency | Common, especially in older adults |
| Deaths | N/A |
Edema refers to the medical condition characterized by the excessive accumulation of fluid within the tissues, most commonly observed in the upper (arms and hands) and lower extremities (legs and feet). This buildup of fluid can lead to swelling and discomfort and is often an indicator of underlying health issues.
Causes of Edema
Edema can develop for a variety of reasons, including:
- Heart Conditions: Poor heart function can result in fluid buildup, especially in the legs.
- Kidney Disease: The kidneys, when not functioning correctly, may not eliminate enough fluid and sodium from the blood, leading to edema.
- Liver Disease: Cirrhosis or other liver conditions can cause fluid to accumulate in the body.
- Pregnancy: Fluid retention is common during pregnancy and can lead to mild swelling.
- Medications: Some medications, including high blood pressure drugs, steroids, and NSAIDs, may cause edema.
- Infections and Injuries: Localized swelling can occur at infection or injury sites.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Beyond visible swelling, individuals with edema may experience:
- Tightness or reduced flexibility in the affected area
- A feeling of heaviness or discomfort
- Pitting (when pressing the swollen area leaves an indent that takes some time to fill back)
Diagnosis often involves:
- Physical examination
- Medical history review
- Ultrasound or MRI for imaging
- Blood tests and urinalysis to check for underlying conditions
Treatment and Management
The approach to treating edema depends on its cause:
- Medications: Diuretics can help increase urine output and reduce fluid buildup.
- Compression: Wearing compression stockings or sleeves can prevent fluid from accumulating.
- Elevation: Raising the affected limb can help drain excess fluid.
- Dietary Changes: Reducing salt intake can help mitigate fluid retention.
Complications
If left untreated, edema can lead to:
- Skin infections or ulcers
- Decreased blood circulation
- Scarring between tissue layers
- Decreased elasticity in affected joints and tissues
Prevention
While not all forms of edema are preventable, the following practices can reduce risks:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Regular exercise
- A balanced diet with limited salt intake
- Avoiding sitting or standing in one position for extended periods
See Also
References
- Guyton, A.C., & Hall, J.E. Textbook of Medical Physiology. Saunders Elsevier, 2016.
- Kapoor, W.N. Current Diagnosis & Treatment: Cardiology. McGraw-Hill Education, 2019.
- Mayo Clinic: Edema
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Kondreddy Naveen, Prab R. Tumpati, MD



