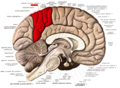
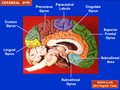
Precuneus
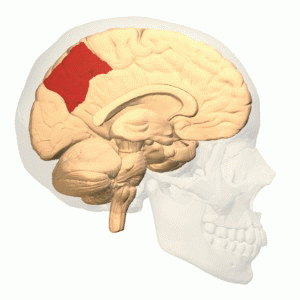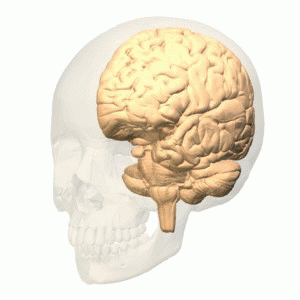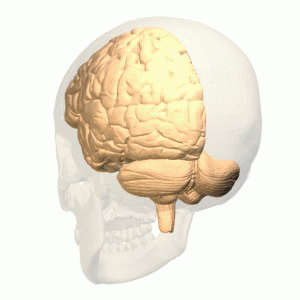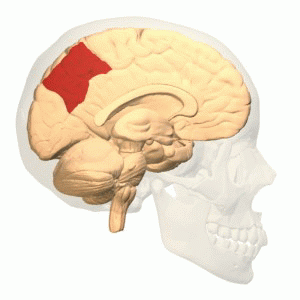
The precuneus is a part of the brain located on the medial surface of the parietal lobe. It is situated between the cuneus and the paracentral lobule, and is bounded anteriorly by the marginal sulcus and posteriorly by the parieto-occipital sulcus. The precuneus is involved in a variety of complex functions, including visuospatial processing, episodic memory, and aspects of consciousness.
Anatomy
The precuneus is a subdivision of the parietal lobe and is located in the medial part of the brain. It is bordered by the cingulate gyrus inferiorly and the superior parietal lobule laterally. The region is supplied by branches of the posterior cerebral artery and the anterior cerebral artery.
Functions
The precuneus is implicated in several high-level cognitive functions:
- Visuospatial Processing: The precuneus plays a crucial role in spatial orientation and the perception of the environment.
- Episodic Memory: It is involved in the retrieval of autobiographical memories and the mental imagery associated with these memories.
- Self-Referential Processing: The precuneus is active during tasks that involve self-reflection and the contemplation of one's own thoughts and feelings.
- Consciousness: Studies have shown that the precuneus is active during states of wakefulness and conscious awareness.
Clinical Significance
Damage to the precuneus can result in a variety of neurological deficits. Lesions in this area can lead to impairments in memory, spatial awareness, and self-perception. Additionally, abnormalities in the precuneus have been associated with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia.
Research
Recent research has focused on the role of the precuneus in the default mode network (DMN), a network of brain regions that are active when the brain is at rest and not focused on the external environment. The precuneus is considered a central node in this network, contributing to the brain's baseline activity and internal thought processes.
Related Pages
- Parietal lobe
- Cuneus
- Paracentral lobule
- Cingulate gyrus
- Superior parietal lobule
- Posterior cerebral artery
- Anterior cerebral artery
- Default mode network
- Alzheimer's disease
- Schizophrenia
This article is a neuroanatomy stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD