Radiation
(Redirected from Radiological)
Radiation refers to the emission and propagation of energy through space or a material medium in the form of waves or particles. It can occur in various forms, ranging from electromagnetic radiation, including light, X-rays, and ultraviolet (UV) radiation, to particle radiation such as alpha and beta particles emitted from radioactive materials.
Types of Radiation
Radiation is commonly categorized into two types: non-ionizing and ionizing radiation.
- Non-ionizing radiation includes forms of electromagnetic radiation that do not carry enough energy to ionize atoms or molecules. Examples include microwaves, radio waves, and visible light.
- Ionizing radiation carries enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, thus creating ions. It includes X-rays, gamma rays, and particle radiation from radioactive decay.
Electromagnetic Radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that is produced by oscillating electric and magnetic fields and travels through space at the speed of light. This category encompasses a wide spectrum of radiation, from very long radio waves to very short gamma rays.
Particle Radiation
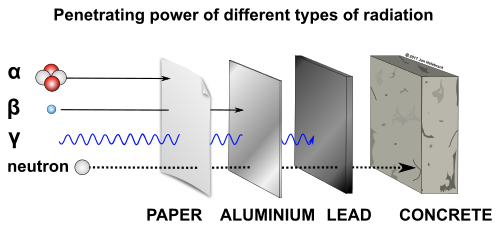
Particle radiation consists of subatomic particles, such as electrons, protons, neutrons, or alpha particles, emitted at high speeds from unstable atoms or nuclear reactions.
Sources of Radiation
Radiation can be derived from both natural and artificial sources. Natural background radiation comes from cosmic rays, radioactive materials in the earth, and naturally occurring radioactive substances within the human body. Artificial radiation sources include medical X-rays, nuclear power plants, and consumer products like smoke detectors and television sets.
Effects of Radiation on Human Health
The biological effects of radiation depend on the type and amount of radiation exposure. Non-ionizing radiation is generally considered less harmful to living tissue, while ionizing radiation can damage biological tissues, leading to skin burns, radiation sickness, cancer, and, at very high doses, death.
Glossary
- Electromagnetic radiation - A form of energy that is propagated through space or through a material medium in the form of electromagnetic waves.
- Ionizing radiation - Radiation with enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, creating ions.
- Non-ionizing radiation - Radiation without enough energy to cause ionization in the matter it interacts with.
- Alpha particles - Positively charged particles consisting of two protons and two neutrons, emitted by certain radioactive materials.
- Beta particles - High-energy, high-speed electrons or positrons emitted by certain types of radioactive nuclei.
- Gamma rays - Penetrating electromagnetic radiation of a kind arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei.
- X-Rays - A form of electromagnetic radiation, similar to light but of shorter wavelength and capable of penetrating solids and ionizing gases.
- Cosmic rays - Extremely high-energy radiation, mainly originating outside the Solar System.
- Radioactive decay - The process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation in the form of particles or electromagnetic waves.
- Radiation sickness - Illness and symptoms resulting from excessive exposure to ionizing radiation.
- Cancer - A disease characterized by the uncontrolled division of abnormal cells in a part of the body.
- Radiation therapy - The use of ionizing radiation to treat cancer by killing cancerous cells or slowing their growth.
- Ultraviolet radiation - A form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength shorter than that of visible light but longer than X-rays.
| Radiation (physics and health) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Elements of nature | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
* Category
|
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD