Granulomatous amoebic encephalitis
(Redirected from Sappinia amoebic encephalitis)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Granulomatous amoebic encephalitis | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Headache, fever, nausea, vomiting, neurological deficits |
| Complications | Seizures, coma, death |
| Onset | Gradual |
| Duration | Progressive |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Acanthamoeba, Balamuthia mandrillaris, Sappinia diploidea |
| Risks | Immunocompromised state, HIV/AIDS, organ transplantation |
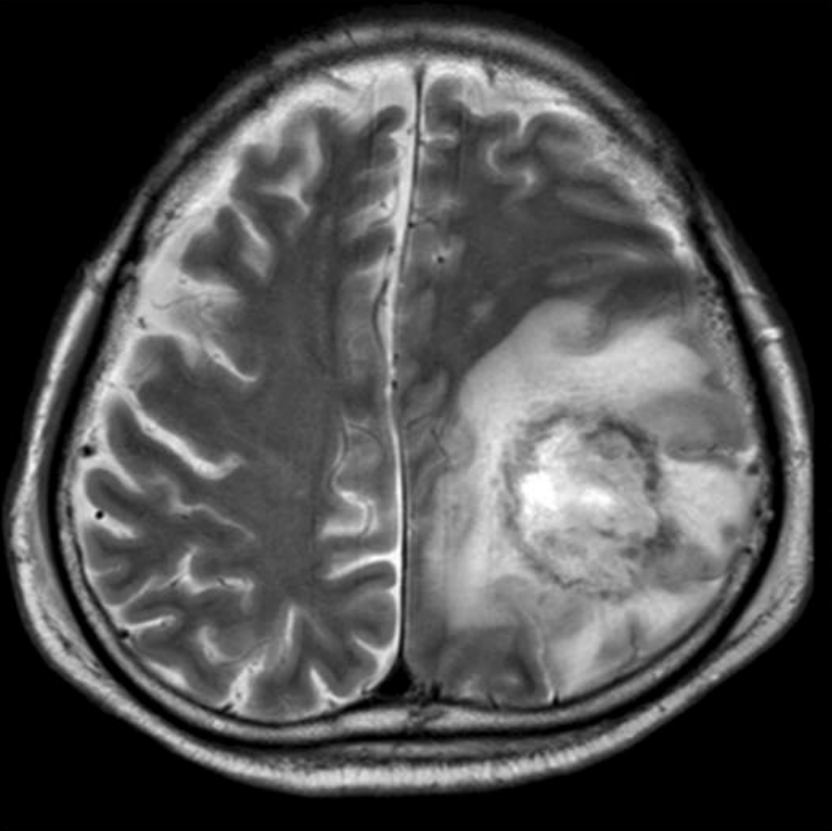
| Diagnosis | Brain biopsy, MRI, CT scan, CSF analysis |
| Differential diagnosis | Bacterial meningitis, viral encephalitis, brain abscess |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Antimicrobial therapy, surgical intervention |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Poor |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Granulomatous Amoebic Encephalitis (GAE) is a rare, often fatal, central nervous system infection caused by certain amoebic species, primarily Acanthamoeba spp., and less frequently by Balamuthia mandrillaris. This condition is characterized by the formation of granulomas, which are inflammatory lesions, in the brain and spinal cord. GAE typically occurs in individuals with compromised immune systems but can also affect healthy persons.
Causes and Transmission
GAE is caused by amoebae, microscopic single-celled organisms, which are commonly found in soil, freshwater, and other environments. The primary amoebae responsible for GAE are:
These amoebae can enter the human body through various routes, such as inhalation of dust containing the amoebae, contamination of skin wounds, or through the nasal passages and eyes. Once inside the body, the amoebae can travel to the central nervous system, leading to GAE.
Symptoms
The symptoms of GAE can vary but often include:
- Headache
- Fever
- Stiff neck
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion
- Loss of coordination
- Seizures
- Coma
Symptoms can progress rapidly, and the disease can be fatal if not treated promptly.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing GAE involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Methods used in the diagnosis include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or Computed Tomography (CT) Scan to detect lesions in the brain.
- Lumbar puncture to analyze cerebrospinal fluid.
- Biopsy of brain tissue.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) testing to identify amoebic DNA.
Treatment
Treatment of GAE is challenging and often involves a combination of antimicrobial agents. The most commonly used medications include:
- Amphotericin B
- Fluconazole or Itraconazole
- Rifampicin
- Sulfadiazine
Early diagnosis and aggressive treatment are crucial for improving outcomes, as the disease progresses rapidly and is often fatal.
Prevention
Preventive measures for GAE are primarily aimed at reducing exposure to the amoebae. Recommendations include:
- Avoiding contact with soil and freshwater sources that may be contaminated.
- Using sterile or distilled water for nasal irrigation.
- Properly cleaning and disinfecting contact lenses.
- Covering skin wounds when in environments where exposure to soil or water is likely.
Epidemiology
GAE is a rare disease, with cases reported worldwide. It primarily affects individuals with compromised immune systems but can also occur in healthy persons. The exact incidence and prevalence of the disease are unknown due to its rarity and the challenges associated with diagnosis.
See Also
- Amoebic Meningoencephalitis
- Acanthamoeba Keratitis
- Balamuthia Amoebic Encephalitis
- Naegleria fowleri
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

