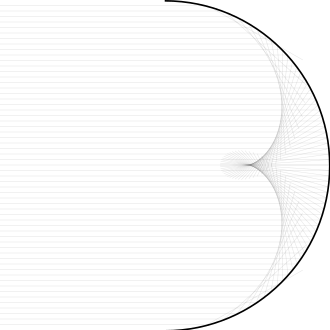
Spherical aberration
Spherical aberration is a type of optical aberration that occurs when light rays passing through a lens or reflecting off a mirror converge at different points, depending on their distance from the optical axis. This phenomenon leads to a blurring of the image, as not all the light focuses to the same point. Spherical aberration is inherent in all spherical optical elements, including the lenses in eyeglasses, camera lenses, and the mirrors in telescopes.
Causes and Effects
The root cause of spherical aberration lies in the geometric shape of spherical lenses and mirrors. These optical elements have a consistent curvature across their surface, which means that light rays striking the lens or mirror near its edge are bent more than those hitting closer to the center. As a result, peripheral rays focus at a shorter distance than central rays, leading to a blurred or distorted image. This effect is particularly noticeable in simple lenses or mirrors with a large aperture and short focal length.
Correction and Minimization
Several methods exist to correct or minimize spherical aberration:
- Using Aspheric Elements: Lenses or mirrors with a non-spherical shape can significantly reduce spherical aberration. Aspheric elements are often used in high-quality optical systems to improve image clarity.
- Lens Combinations: Combining multiple lenses with different shapes and refractive properties can counteract the effects of spherical aberration. This approach is common in complex optical systems like microscopes and telescopes.
- Aperture Reduction: Reducing the aperture size of an optical system limits the angle of incoming light rays, minimizing the impact of spherical aberration. However, this method also reduces the amount of light entering the system, which can be a disadvantage in low-light conditions.
- Software Correction: In digital imaging systems, software algorithms can correct spherical aberration after image capture. This method is increasingly used in digital cameras and smartphones.
Applications and Importance
Understanding and correcting spherical aberration is crucial in the design of optical systems where image clarity is important. In astronomy, for example, telescopes need to minimize spherical aberration to clearly resolve distant celestial objects. In photography, lenses designed to reduce spherical aberration contribute to sharper images. Moreover, in fields such as ophthalmology, correcting spherical aberration in eyeglasses and contact lenses can significantly improve vision quality.
Historical Context
The study of spherical aberration dates back to the early days of optical science. Notable scientists like Isaac Newton and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz explored the nature of spherical aberration in their work. The development of aspheric lenses and other corrective techniques has been a key focus of optical engineering for centuries, reflecting the ongoing importance of addressing spherical aberration in various technologies.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD