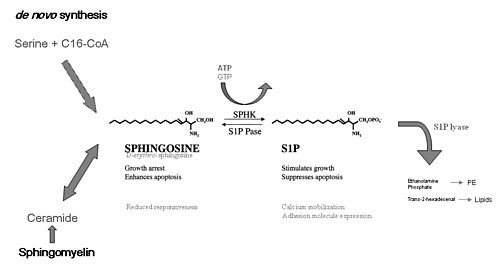
Sphingosine kinase
Sphingosine kinase (SphK) is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the metabolism of sphingolipids, which are a class of lipids involved in various cellular functions, including cell proliferation, survival, migration, and inflammation. There are two main isoforms of this enzyme, sphingosine kinase 1 (SphK1) and sphingosine kinase 2 (SphK2), which differ in their tissue distribution, cellular localization, and specific functions within the cell.
Function
Sphingosine kinase catalyzes the phosphorylation of sphingosine to form sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), a potent signaling molecule that exerts its effects by binding to a family of G protein-coupled receptors known as S1P receptors. This reaction is a key step in the sphingolipid signaling pathway, which is involved in regulating a variety of cellular processes. S1P acts as a second messenger in signal transduction and has been implicated in processes such as angiogenesis, immune cell trafficking, and the regulation of apoptosis.
Isoforms
Sphingosine Kinase 1
SphK1 is predominantly found in the cytoplasm and is translocated to the plasma membrane upon activation, where it interacts with its substrates and other signaling molecules. It is widely expressed in various tissues and has been shown to play a role in promoting cell survival and proliferation. Overexpression of SphK1 has been observed in several types of cancer, suggesting its involvement in tumorigenesis.
Sphingosine Kinase 2
SphK2 is located in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus of cells. It has a broader tissue distribution compared to SphK1 and is involved in the regulation of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. SphK2 has been found to have both pro-survival and pro-apoptotic functions, depending on the cellular context and the signaling pathways involved.
Clinical Significance
The sphingosine kinase/S1P signaling axis has been identified as a potential target for therapeutic intervention in various diseases, including cancer, inflammatory diseases, and cardiovascular diseases. Inhibitors of SphK1 and SphK2 are being explored as potential drugs for the treatment of these conditions. Additionally, the role of SphK1 in cancer progression and its potential as a biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis are areas of active research.
Research Tools
Research into the functions and regulation of sphingosine kinase has been facilitated by the development of specific inhibitors and genetic tools such as knockout mice. These tools have helped to elucidate the complex roles of SphK isoforms in health and disease.
This article is a biochemistry stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD