Tautomer
Tautomerism is a phenomenon in chemistry where molecules with the same molecular formula exist in multiple forms by the shifting of atomic positions within the molecule. These different forms, known as tautomers, are structural isomers that rapidly interconvert, typically in a dynamic equilibrium. The most common type of tautomerism involves the relocation of a proton (H+) and is called prototropic tautomerism. Other types include valence tautomerism and ring-chain tautomerism, among others. Tautomerism plays a crucial role in various biological processes and has significant implications in organic synthesis, drug design, and biochemistry.
Types of Tautomerism
Tautomerism can be classified into several types based on the nature of the atomic or group transfer. The most notable types include:
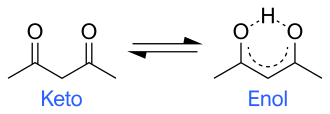
- Prototropic Tautomerism: This is the most common form, where tautomers differ by the position of a proton and a double bond. The keto-enol tautomerism, where a ketone form (keto) and an enolic form (enol) interconvert, is a classic example.
- Valence Tautomerism: In this type, the rearrangement involves changes in the connectivity of electrons within a molecule, leading to different bonding patterns.
- Ring-Chain Tautomerism: This involves the interconversion between cyclic and acyclic forms. It is common in sugars and other cyclic compounds.
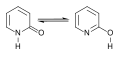
- Tautomeric Pairs: Specific pairs of tautomers, such as imine-enamine, lactam-lactim, and nitroso-oxime, demonstrate the diversity of tautomerism.
Mechanism and Conditions
The tautomerization process involves the breaking and forming of chemical bonds, typically under the influence of a catalyst or specific conditions like pH changes. The mechanism can vary significantly depending on the type of tautomerism and the involved functional groups. For prototropic tautomerism, the presence of acidic or basic conditions can facilitate the proton transfer.
Biological Significance
Tautomerism has profound implications in biology. The tautomeric forms of nucleobases in DNA can lead to mutations during DNA replication. Additionally, enzyme specificity and drug-receptor interactions can be influenced by the tautomeric states of molecules, affecting the efficacy and metabolism of pharmaceuticals.
Applications in Organic Synthesis and Drug Design
In organic chemistry, controlling tautomerism is essential for the synthesis of desired compounds. Tautomeric equilibrium can influence the reactivity and stability of intermediates. In drug design, understanding tautomerism is crucial for predicting the bioactive form of a molecule, optimizing drug-target interactions, and minimizing off-target effects.
Gallery
See Also
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD