Tricarboxylic acid
Tricarboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain three carboxyl functional groups (-COOH). These acids are important in various biochemical processes, most notably in the citric acid cycle, also known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle or Krebs cycle, which is a key metabolic pathway that unifies carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism.
Structure and Properties
Tricarboxylic acids are characterized by the presence of three carboxyl groups. These groups can donate protons, making the compounds acidic. The general formula for a tricarboxylic acid is C₆H₈O₇, although variations exist depending on the specific structure of the acid.
Citric Acid
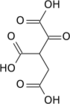
Citric acid is one of the most well-known tricarboxylic acids. It is a weak organic acid that is a natural preservative and is also used to add an acidic or sour taste to foods and drinks. Citric acid is a key intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in the metabolism of all aerobic organisms.
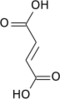
Cis-Aconitic Acid
Cis-aconitic acid is formed from citric acid by the removal of a molecule of water. It is then converted to isocitric acid by the addition of water.
Trans-Aconitic Acid
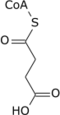
Isocitric Acid
Isocitric acid is an isomer of citric acid. It is also an intermediate in the citric acid cycle. The conversion of citric acid to isocitric acid is catalyzed by the enzyme aconitase.
Aconitic Acid
Aconitic acid exists in two isomeric forms: cis-aconitic acid and trans-aconitic acid. These acids are intermediates in the conversion of citric acid to isocitric acid in the citric acid cycle.
Trans-aconitic acid is a less common isomer of aconitic acid. It is not typically involved in the citric acid cycle but can be found in some plant species.
Biological Importance
Tricarboxylic acids play a crucial role in the citric acid cycle, which is essential for the production of energy in aerobic organisms. This cycle is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
Related Pages
Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
| + H2O
|
NADH +H+
NAD+ H2O FADH2
FAD CoA + ATP (GTP)
Pi + ADP (GDP) | |
| NADH + H+ + CO2
| ||
| CoA | NAD+ | |
Lua error in package.lua at line 80: module 'strict' not found.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD