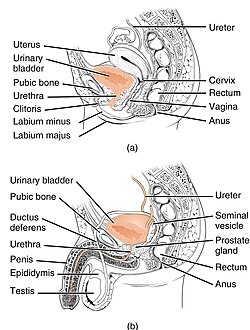
Urinary incontinence
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
Urinary incontinence is a common medical condition that involves a loss of bladder control, resulting in involuntary leakage of urine. It's an often embarrassing problem and prevalence increases with age, especially affecting women more than men.
Introduction
Urinary incontinence is not a disease in itself but is a symptom of underlying medical conditions, lifestyle habits, or physical problems. It can range from occasionally leaking urine when you cough or sneeze to having an urge to urinate that's so sudden and strong you don't get to a toilet in time.
Types of Urinary Incontinence
- Urinary incontinence is typically divided into several types:
- Stress Incontinence: Leakage of urine during physical activities that increase abdominal pressure such as coughing, sneezing, laughing, or lifting heavy objects.
- Urge Incontinence: Also known as overactive bladder, characterized by a sudden, intense urge to urinate followed by an involuntary loss of urine.
- Overflow Incontinence: Characterized by the inability to empty the bladder completely, leading to frequent or constant dribbling of urine.
- Functional Incontinence: Occurs when physical or mental impairments prevent a person from reaching the toilet in time.
- Mixed Incontinence: When a person experiences more than one type of urinary incontinence.
Causes and Risk Factors
Causes of urinary incontinence can be temporary or persistent. Temporary causes include certain drinks, foods and medications that act as diuretics. Persistent urinary incontinence may be due to underlying physical problems or changes such as aging, hysterectomy, enlarged prostate, or neurological disorders.
Diagnosis
The process of diagnosing urinary incontinence typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, bladder diary, and tests such as urinalysis, bladder scan, and urodynamic testing. In some cases, more specialized tests like cystoscopy or imaging tests may be performed.
Treatment
Treatment for urinary incontinence is tailored to the type of incontinence, the severity of symptoms, and the underlying cause. It can range from lifestyle changes, bladder training, pelvic floor muscle exercises, medications, medical devices, interventional therapies to surgery.
Prognosis
The outlook for urinary incontinence depends on its cause. With appropriate management and treatment, most people with this condition can achieve significant relief or even a complete resolution of symptoms.
References
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD