Superior vena cava syndrome
(Redirected from Vena cava superior syndrome)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Superior vena cava syndrome | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
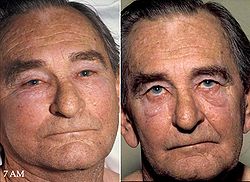
| Symptoms | Swelling of face, neck, and upper limbs, dyspnea, cough, chest pain |
| Complications | Cerebral edema, airway obstruction |
| Onset | Gradual or sudden |
| Duration | Variable |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Malignancy (e.g., lung cancer, lymphoma), thrombosis, infection |
| Risks | Smoking, central venous catheter placement |
| Diagnosis | CT scan, MRI, venography |
| Differential diagnosis | Heart failure, pericardial effusion, tracheal compression |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Radiation therapy, chemotherapy, stenting, corticosteroids |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Depends on underlying cause |
| Frequency | Rare |
| Deaths | N/A |
Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
Superior Vena Cava Syndrome (SVCS) is a significant medical condition characterized by the obstruction of blood flow in the superior vena cava. This obstruction is typically caused by factors such as a malignant neoplasm, thrombosis, or an aneurysm. SVCS is considered a medical emergency and necessitates immediate treatment due to the critical role of the superior vena cava in returning deoxygenated blood from the upper body to the heart.
Signs and Symptoms
The clinical manifestations of Superior Vena Cava Syndrome include:
- Swelling of the face, neck, and upper arms
- Cyanosis, a bluish discoloration of the skin, particularly evident in the aforementioned areas
- Persistent cough
- Orthopnea, difficulty in breathing that is experienced while lying flat
- Severe headache
These symptoms result from the increased venous pressure and reduced blood return to the heart.
Causes
The primary causes of SVCS include:
- Malignant Neoplasm: Tumors, particularly lung cancer or lymphoma, can compress or invade the superior vena cava.
- Thrombosis: Blood clots within the vein can lead to obstruction.
- Aneurysm: An abnormal bulge in the wall of the vein can impede blood flow.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of SVCS involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies. Commonly employed imaging techniques include:
These imaging modalities help in identifying the location and cause of the obstruction.
Treatment
Treatment of SVCS aims at relieving the symptoms and addressing the underlying cause. Therapeutic approaches include:
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer-related SVCS.
- Anticoagulation therapy for thrombosis.
- Surgical interventions in certain cases, such as stent placement.
See Also
External Links
- Mayo Clinic: Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
- National Center for Biotechnology Information: Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
References
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Kondreddy Naveen, Prab R. Tumpati, MD


