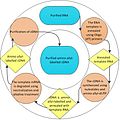
Aminoallyl nucleotide
Aminoallyl Nucleotide
Aminoallyl nucleotides are modified nucleotides that contain an aminoallyl group attached to the nucleotide base. These modified nucleotides are commonly used in molecular biology and biochemistry for labeling nucleic acids with fluorescent dyes or other detectable markers.
Structure
Aminoallyl nucleotides are derived from standard nucleotides by the addition of an aminoallyl group. This group is typically attached to the base of the nucleotide, such as adenine, cytosine, guanine, or uracil. The aminoallyl group provides a reactive amine that can be used for conjugation with various labels.
Applications
Aminoallyl nucleotides are primarily used in the labeling of DNA and RNA for various applications, including:
- Microarray Analysis: Aminoallyl nucleotides are incorporated into cDNA during reverse transcription. The aminoallyl-modified cDNA can then be labeled with fluorescent dyes for use in DNA microarrays.
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH): These nucleotides can be used to label probes for FISH, allowing for the visualization of specific DNA sequences within chromosomes.
- Quantitative PCR (qPCR): Aminoallyl nucleotides can be used to label probes or primers in qPCR assays, facilitating the detection and quantification of target sequences.
Synthesis
The synthesis of aminoallyl nucleotides involves the chemical modification of standard nucleotides. Typically, the aminoallyl group is introduced through a chemical reaction that attaches the group to the nucleotide base. This process requires careful control to ensure that the nucleotide retains its ability to pair with complementary bases.
Advantages
Aminoallyl nucleotides offer several advantages in molecular biology applications:
- Versatility: The reactive amine group allows for the attachment of a wide range of labels, including fluorescent dyes, biotin, and other markers.
- Stability: The modified nucleotides are generally stable and can be incorporated into nucleic acids without disrupting their function.
- Efficiency: The labeling process is efficient, allowing for high levels of incorporation and strong signal generation.
Limitations
While aminoallyl nucleotides are highly useful, they also have some limitations:
- Complex Synthesis: The chemical synthesis of aminoallyl nucleotides can be complex and requires specialized reagents and conditions.
- Potential for Interference: The presence of the aminoallyl group may interfere with some biological processes, although this is generally minimal.
Related Pages
| Molecular biology | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD