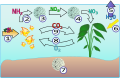
Ammonia poisoning
Ammonia Poisoning
Ammonia poisoning occurs when a person is exposed to excessive amounts of ammonia, a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula NH_. Ammonia is a colorless gas with a characteristic pungent smell and is commonly found in household cleaners, industrial applications, and as a byproduct of agricultural activities.
Causes
Ammonia poisoning can result from inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact with ammonia. Common sources of exposure include:
- Household cleaners: Many cleaning products contain ammonia, which can be harmful if inhaled or ingested.
- Industrial exposure: Workers in industries such as agriculture, refrigeration, and chemical manufacturing may be exposed to ammonia.
- Agricultural activities: Ammonia is used as a fertilizer and can be released into the air during its application.
- Accidental release: Spills or leaks from storage tanks or transportation accidents can lead to high levels of ammonia in the environment.
Symptoms
The symptoms of ammonia poisoning vary depending on the route of exposure and the concentration of ammonia. Common symptoms include:
- Respiratory distress: Coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing due to irritation of the respiratory tract.
- Eye irritation: Redness, tearing, and burning sensation in the eyes.
- Skin irritation: Redness, itching, and burns on the skin upon contact with liquid ammonia.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain if ammonia is ingested.
- Neurological effects: Headache, dizziness, and confusion in severe cases.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of ammonia poisoning is based on the patient's history of exposure and clinical symptoms. Medical professionals may perform the following:
- Physical examination: To assess the extent of irritation and damage to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract.
- Blood tests: To measure ammonia levels in the blood and assess the severity of poisoning.
- Pulmonary function tests: To evaluate respiratory function if inhalation exposure is suspected.
Treatment
Treatment for ammonia poisoning focuses on removing the source of exposure and providing supportive care:
- Decontamination: Remove contaminated clothing and wash affected skin with water.
- Oxygen therapy: Administer oxygen to patients with respiratory distress.
- Bronchodilators: Use medications to relieve bronchospasm and improve breathing.
- Intravenous fluids: Provide fluids to maintain hydration and support circulation.
- Symptomatic treatment: Address specific symptoms such as pain or nausea.
Prevention
Preventing ammonia poisoning involves minimizing exposure and implementing safety measures:
- Personal protective equipment: Use appropriate gear such as masks, gloves, and goggles when handling ammonia.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in areas where ammonia is used or stored.
- Training and education: Provide training for workers on the safe handling and storage of ammonia.
- Emergency preparedness: Develop and practice emergency response plans for ammonia spills or leaks.
Related Pages
| Toxicology | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD