Cartilage–hair hypoplasia
(Redirected from Cartilage-hair hypoplasia)
| Cartilage–hair hypoplasia | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | N/A |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | N/A |
| Duration | N/A |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | N/A |
| Risks | N/A |
| Diagnosis | N/A |
| Differential diagnosis | N/A |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | N/A |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | N/A |
| Deaths | N/A |
Cartilage–hair hypoplasia (CHH) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by short stature, fine and sparse hair, and immunodeficiency. It is a form of skeletal dysplasia and is associated with anemia and an increased risk of certain cancers.
Genetics
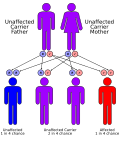
CHH is caused by mutations in the RMRP gene, which is located on chromosome 9. This gene is responsible for encoding a non-coding RNA component of the mitochondrial RNA processing endoribonuclease. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning that an individual must inherit two copies of the mutated gene to be affected.
Clinical Features
Individuals with CHH typically present with short stature due to metaphyseal dysplasia, which affects the growth of long bones. Hair is often sparse, fine, and light-colored. The condition is also associated with immunodeficiency, leading to increased susceptibility to infections. Some individuals may develop anemia and have an increased risk of developing certain types of cancer, such as lymphoma and basal cell carcinoma.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of CHH is based on clinical features, family history, and genetic testing to identify mutations in the RMRP gene. Radiographic imaging can reveal characteristic skeletal abnormalities, and blood tests can assess immune function and detect anemia.
Management
Management of CHH involves a multidisciplinary approach, including regular monitoring of growth and development, management of infections, and surveillance for malignancies. Growth hormone therapy may be considered in some cases to improve growth. Bone marrow transplantation may be an option for individuals with severe immunodeficiency.
Epidemiology
CHH is most commonly found in the Amish and Finnish populations, but it can occur in any ethnic group. The prevalence is estimated to be 1 in 23,000 in the Finnish population.
See also
References
External links
| Skeletal disorders | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This skeletal disorder related article is a stub.
|
| Genetic disorders relating to deficiencies of transcription factor or coregulators | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Deepika vegiraju, Prab R. Tumpati, MD