Defatting (medical)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Defatting | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | Defatting dermatitis |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Dry skin, irritation, redness, cracking of the skin |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | N/A |
| Duration | N/A |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Exposure to solvents such as kerosene, gasoline, turpentine, and detergents |
| Risks | Occupational exposure, frequent hand washing |
| Diagnosis | N/A |
| Differential diagnosis | N/A |
| Prevention | Use of protective gloves, moisturizers, and barrier creams |
| Treatment | Emollients, topical corticosteroids |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Good with avoidance of irritants and proper skin care |
| Frequency | Common in certain occupations |
| Deaths | N/A |
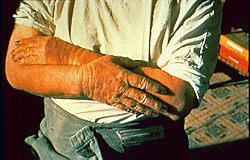
Defatting is a medical term that refers to the removal of fat from the skin or tissue. This process can occur due to various factors, including exposure to certain chemicals, excessive washing, or medical procedures. Defatting can lead to skin irritation, dryness, and other dermatological issues.
Causes
Defatting of the skin can be caused by:
- Chemical exposure: Certain chemicals, such as solvents, can strip the skin of its natural oils.
- Frequent washing: Excessive washing with soap and water can remove the protective lipid layer of the skin.
- Medical procedures: Some medical treatments and procedures may involve the removal of fat from tissues.
Symptoms
The symptoms of defatting include:
Prevention
To prevent defatting, it is important to:
- Use mild, non-irritating cleansers.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to harsh chemicals.
- Apply moisturizers regularly to maintain skin hydration.
- Wear protective gloves when handling chemicals.
Treatment
Treatment for defatting typically involves:
- Discontinuing exposure to the causative agent.
- Using emollients and moisturizers to restore the skin's natural barrier.
- Applying topical steroids or other medications to reduce inflammation and irritation.
Related Topics
See Also
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

