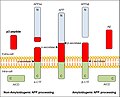
P3 peptide
P3 Peptide is a short chain of amino acids that is significant in the field of biochemistry and medicine, particularly in the study of immune system responses and vaccine development. The P3 peptide has been identified as a critical component in various biological processes, including the modulation of immune responses and the potential treatment of certain diseases.
Overview
Peptides are short chains of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. They play crucial roles in many biological functions, acting as hormones, neurotransmitters, growth factors, and antigens. The P3 peptide, specifically, has garnered interest for its unique properties and its potential applications in immunotherapy and vaccine design.
Structure and Function
The structure of P3 peptide consists of a specific sequence of amino acids that determines its function and its interaction with other molecules in the body. This peptide can mimic certain parts of a pathogen's structure, making it a valuable tool for vaccine development. By introducing the P3 peptide into the body, it is possible to stimulate the immune system to recognize and fight the actual pathogen more effectively.
Applications in Medicine
One of the primary applications of P3 peptide is in the development of vaccines. By using peptides that mimic parts of a pathogen, researchers can create vaccines that are both safe and effective. This approach has been explored for various diseases, including influenza, HIV, and certain types of cancer.
In addition to vaccine development, P3 peptide has potential applications in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. By modulating the immune response, peptides can help reduce inflammation and prevent the immune system from attacking the body's own tissues.
Research and Development
Research on P3 peptide is ongoing, with scientists exploring its potential in various medical applications. Studies have focused on understanding the peptide's structure-function relationships, optimizing its delivery to the immune system, and evaluating its safety and efficacy in clinical trials.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the promising potential of P3 peptide, there are challenges to overcome. These include ensuring the stability of the peptide, achieving targeted delivery to the immune system, and minimizing potential side effects. Future research will likely focus on addressing these challenges and expanding the applications of P3 peptide in medicine.
Conclusion
P3 peptide represents a promising area of research in biochemistry and medicine, with potential applications in vaccine development and the treatment of autoimmune diseases. As research progresses, the understanding of P3 peptide's role in the immune system and its potential therapeutic applications will continue to expand, offering new possibilities for disease prevention and treatment.
P3_peptide
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD