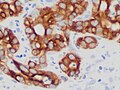
Cholangiocarcinoma
(Redirected from Biliary tract cancer)
Bile duct adenocarcinoma
| Cholangiocarcinoma | |
|---|---|
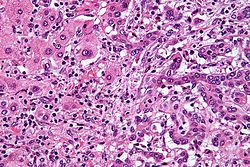
| |
| Synonyms | Bile duct cancer, cancer of the bile duct |
| Pronounce | koh-LAN-jee-oh-KAR-sih-NOH-muh |
| Field | Oncology |
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, yellowish skin, weight loss, generalized itching, fever |
| Complications | |
| Onset | 70 years old |
| Duration | |
| Types | Intrahepatic, perihilar, distal |
| Causes | |
| Risks | Primary sclerosing cholangitis, ulcerative colitis, infection with certain liver flukes, some congenital liver malformations |
| Diagnosis | Confirmed by examination of the tumor under a microscope |
| Differential diagnosis | |
| Prevention | |
| Treatment | Surgical resection, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, stenting procedures, liver transplantation |
| Medication | |
| Prognosis | Generally poor |
| Frequency | 1–2 people per 100,000 per year (Western world) |
| Deaths | |
Cholangiocarcinoma, colloquially known as bile duct cancer, is a rare but serious form of cancer that arises in the bile ducts. These ducts are a series of intricate channels responsible for transporting bile – a fluid aiding in the digestion and absorption of fats – from the liver to the gallbladder and intestines.
Anatomy: Bile Ducts
The bile duct system consists of a series of small tubes that transport bile from the liver to the gallbladder and then into the small intestine. This complex network comprises intrahepatic bile ducts (within the liver), extrahepatic bile ducts (outside the liver), and the common bile duct.
Types of Cholangiocarcinoma
Cholangiocarcinomas are classified based on their location in the bile duct system:
- Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: These originate in the small bile duct branches inside the liver.
- Perihilar (or Klatskin tumor) Cholangiocarcinoma: These form at the hilum, where the left and right hepatic ducts have joined and are leaving the liver.
- Distal Cholangiocarcinoma: These occur further down the bile duct, closer to the small intestine.
Risk Factors
Several conditions are linked to an increased risk of developing cholangiocarcinoma:
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis: An inflammatory disease of the bile ducts that can lead to scarring and narrowing.
- Ulcerative colitis: A chronic condition characterized by inflammation of the large intestine (colon and rectum).
- Cirrhosis: Scarring of the liver due to various causes such as alcoholism or chronic hepatitis.
- Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C: Viral infections that can cause chronic liver disease and cirrhosis.
- Parasitic infection: Particularly infection with liver flukes which are common in certain parts of Asia.
- Congenital liver malformations: Such as Caroli's syndrome and choledochal cysts.
Signs and Symptoms
The clinical presentation of cholangiocarcinoma can be quite variable, and symptoms typically do not appear until the disease has progressed significantly. Common symptoms may include:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Abdominal pain, particularly in the upper right quadrant
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Itching
- Dark urine and pale stools
Investigations
Diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma often involves a combination of blood tests, imaging studies, and, in some cases, biopsy. Liver function tests can detect signs of liver damage or disease, while tumor markers can help identify potential cancer. Imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT, MRI, and ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) can help visualize the bile ducts and detect any abnormalities. A biopsy may be required to confirm the diagnosis.
Staging
Staging is an important process that determines the extent of cancer spread. This information can help guide treatment decisions and prognosis. The TNM (Tumor, Nodes, Metastasis) system is commonly used in the staging of cholangiocarcinoma.
Prognosis and Treatment
The prognosis of cholangiocarcinoma is generally poor due to late diagnosis. Treatment depends on the stage and location of the cancer and can include surgery (if the tumor is localized and the patient is fit for surgery), chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and palliative care.
| This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it! | |
|---|---|
| Digestive system neoplasia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Glandular and epithelial cancer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD