Non-coding RNA
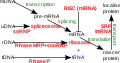
Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a type of RNA that does not encode a protein, but has functions of its own. Non-coding RNAs play various roles in the cell, including regulation of gene expression, organization of chromosome structure, and alteration of protein activity.
Types of Non-coding RNA
There are several types of non-coding RNAs, each with distinct functions. These include:
- MicroRNA (miRNA): These are small non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. They bind to messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and prevent them from being translated into proteins.
- Small interfering RNA (siRNA): These are double-stranded non-coding RNAs that interfere with the expression of specific genes. They do this by degrading mRNA after it has been transcribed.
- Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA): These are longer RNA molecules that regulate gene expression at various levels, including transcription and post-transcriptional processing.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): This is a component of the ribosome, the cellular machinery that translates mRNA into protein.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): This is involved in the process of translation, carrying amino acids to the ribosome to be added to the growing protein chain.
Function of Non-coding RNA
Non-coding RNAs have a wide range of functions in the cell. They are involved in the regulation of gene expression, the modification of proteins, the organization of chromosomes, and many other processes. Some non-coding RNAs, such as miRNAs and siRNAs, regulate gene expression by binding to mRNA molecules and preventing them from being translated into proteins. Others, such as lncRNAs, can interact with proteins and other molecules to regulate gene expression at the level of transcription.
Role in Disease
Alterations in the function of non-coding RNAs have been implicated in a number of diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and cardiovascular diseases. For example, changes in the expression levels of certain miRNAs have been associated with the development and progression of cancer. Similarly, mutations in lncRNAs have been linked to neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
See Also
This RNA related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD