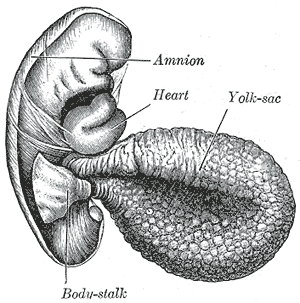
Vitelline circulation
Vitelline circulation refers to the system of blood vessels that is associated with the yolk sac of a developing embryo. This circulatory system is crucial during the early stages of embryonic development, providing nutrients and oxygen to the growing embryo before the establishment of the placental circulation.
Development
The vitelline circulation begins to form during the third week of embryonic development. The yolk sac, which is an extra-embryonic membrane, is connected to the midgut of the embryo via the vitelline duct. Blood islands, which are clusters of hemangioblasts, form within the yolk sac and give rise to the vitelline blood vessels.
Vitelline Arteries and Veins
The vitelline circulation consists of vitelline arteries and veins:
- Vitelline arteries arise from the dorsal aorta and supply blood to the yolk sac.
- Vitelline veins return nutrient-rich blood from the yolk sac to the sinus venosus of the developing heart.
Function
The primary function of the vitelline circulation is to transport nutrients from the yolk sac to the embryo. This system is essential for the survival and growth of the embryo during the early stages of development, before the placenta becomes fully functional.
Transformation
As the embryo continues to develop, the vitelline circulation undergoes significant changes. The vitelline arteries contribute to the formation of the celiac artery, superior mesenteric artery, and inferior mesenteric artery. The vitelline veins contribute to the formation of the portal vein and the hepatic sinusoids.
Clinical Significance
Abnormalities in the development of the vitelline circulation can lead to congenital anomalies such as Meckel's diverticulum, which is a remnant of the vitelline duct. Other potential issues include malformations of the portal vein and associated structures.
Related Pages
- Embryonic development
- Yolk sac
- Placental circulation
- Vitelline duct
- Portal vein
- Meckel's diverticulum
| Human embryogenesis in the first three weeks | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD