Podocyte
(Redirected from Podocytes)
Podocyte
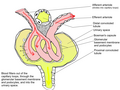
A Podocyte is a type of cell found in the kidney, specifically in the Bowman's capsule of the glomerulus. These cells play a crucial role in the body's ability to filter blood and create urine.
Structure
Podocytes are unique in their structure, featuring a large cell body with primary processes and secondary foot processes, or pedicels. These foot processes interdigitate with those of neighboring podocytes and are connected by a thin filtration slit diaphragm. This structure allows for the efficient filtration of blood.
Function
The primary function of podocytes is to filter blood in the glomerulus, a network of small blood vessels in the kidney. They do this by forming a barrier that prevents the passage of large molecules, such as proteins, while allowing smaller molecules, such as water and salts, to pass through. This filtration process is essential for the production of urine.
Clinical significance
Damage to podocytes can lead to a number of kidney diseases, including Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) and Minimal change disease (MCD). These conditions can result in proteinuria, the presence of excess proteins in the urine, and can ultimately lead to kidney failure.
Research
Research into podocytes has increased our understanding of kidney function and disease. For example, studies have shown that podocytes can regenerate and repair themselves, which has implications for the treatment of kidney diseases. Furthermore, research is ongoing into the genetic and molecular mechanisms that regulate podocyte function and health.
See also
| This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it! | |
|---|---|
References
External links
- Podocyte Biology and Pathogenesis of Kidney Disease at the US National Library of Medicine
- Podocyte-specific knockout of the adaptor protein CD2-associated protein promotes proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis in mice at Kidney International
| Urinary system - Kidney - edit |
|---|
| Renal capsule | Renal cortex | Renal medulla (Renal sinus, Renal pyramids) | Renal calyx | Renal pelvis |
| Nephron - Renal corpuscle (Glomerulus, Bowman's capsule) → Proximal tubule → Loop of Henle → Distal convoluted tubule → Collecting ducts
Juxtaglomerular apparatus (Macula densa, Juxtaglomerular cells) Renal circulation - Renal artery → Interlobar arteries → Arcuate arteries → Cortical radial arteries → Afferent arterioles → Glomerulus → Efferent arterioles → Vasa recta → Arcuate vein → Renal vein |
| Renal physiology |
| Filtration - Ultrafiltration | Countercurrent exchange
Hormones effecting filtration - Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) | Aldosterone | Atrial natriuretic peptide Endocrine - Renin | Erythropoietin (EPO) | Calcitriol (Active vitamin D) | Prostaglandins |
| Assessing Renal function / Measures of Dialysis |
| Glomerular filtration rate | Creatinine clearance | Renal clearance ratio | Urea reduction ratio | Kt/V | Standardized Kt/V | Hemodialysis product |
This article is a cell biology stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Transform your life with W8MD's budget GLP-1 injections from $125.
W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $125 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD